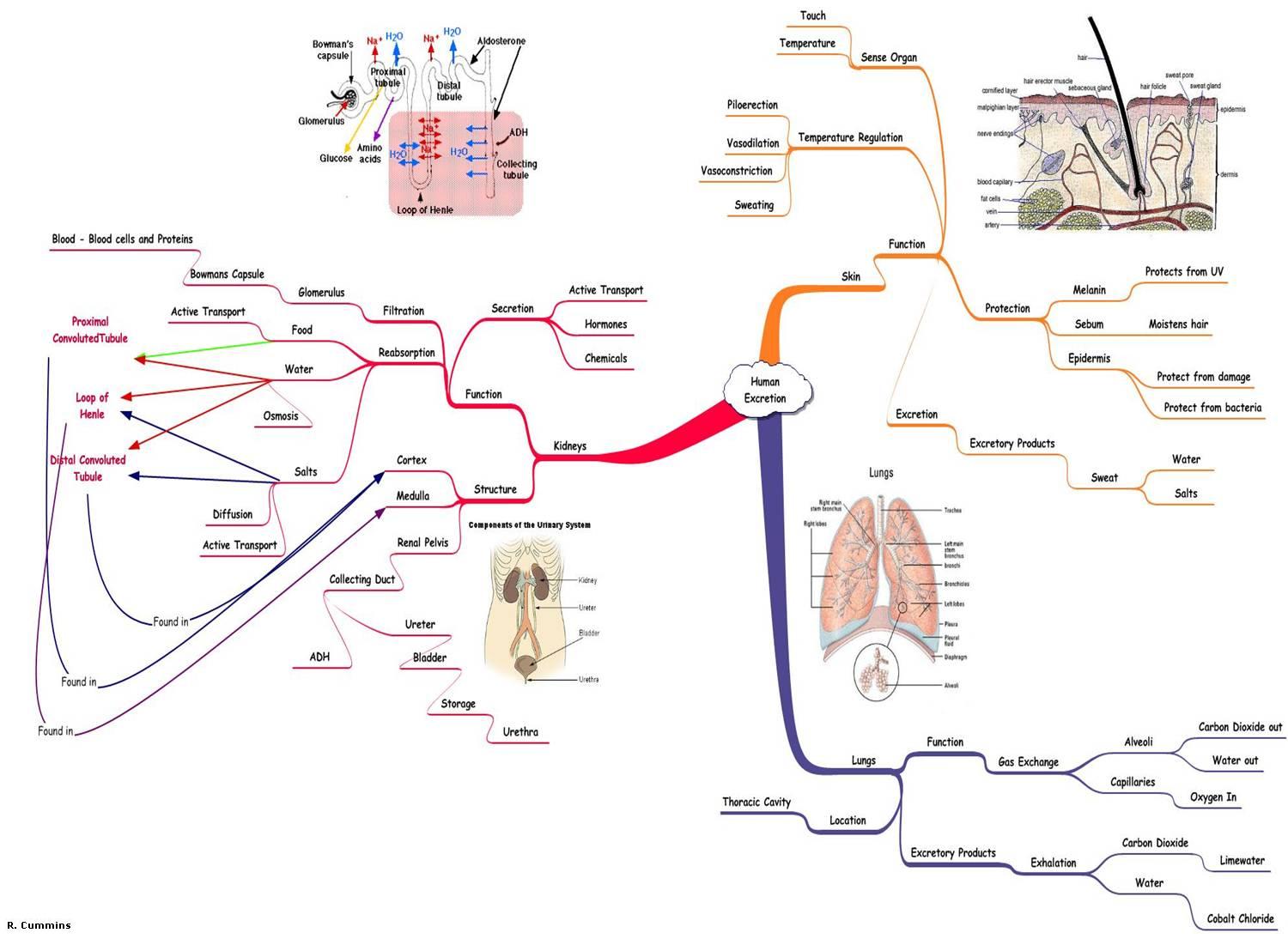
Excretion
The removal of waste products from the body
Homestasis is the maintenance of a stable internal environment in an organism
- Ectotherms are animals that obtain their heat from external sources
- Endotherms generate their heat with their own body reactions
The main excretory organs are:
- lungs (water and carbon dioxide)
- skin (water and salts)
- kidneys (water, salts, and urea)
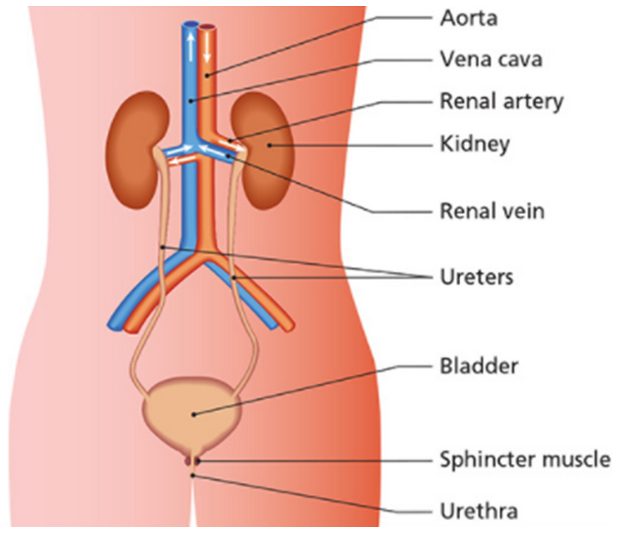
Kidney
The functions of the kidneys are
- excretion of water, salts, and urea
- osmoregulation:
- control the water content of the blood
- control the salt concentration of the blood
- control the pH of the blood (and body fluids)
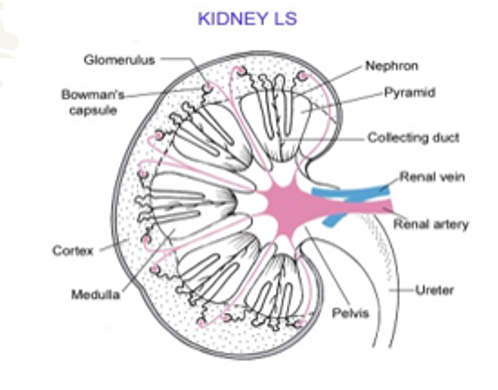
The kidneys make urine in the following way
- blood (containing waste (urea, uric acid, excess salt and water)) enters the kidneys through the renal arteries
- the kidneys filter waste and useful materials from the blood
- useful materials are reabsorbed from the kidneys back into the blood
- some materials are secreted from the blood into the kidneys
- urine formed in the kidneys flows to the bladder through the ureters
- blood (low in waste) leaves the kidneys in the renal veins
- The bladder stores urine
- Urine is excreted through the urethra
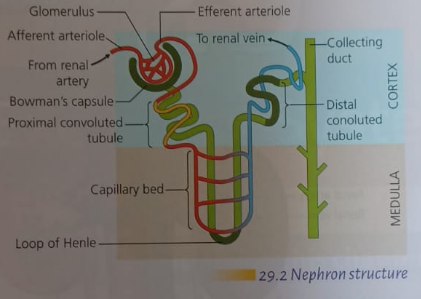
Nephrons
- carry out the functions of the kidneys
- are located in the cortex and medulla of the kidney
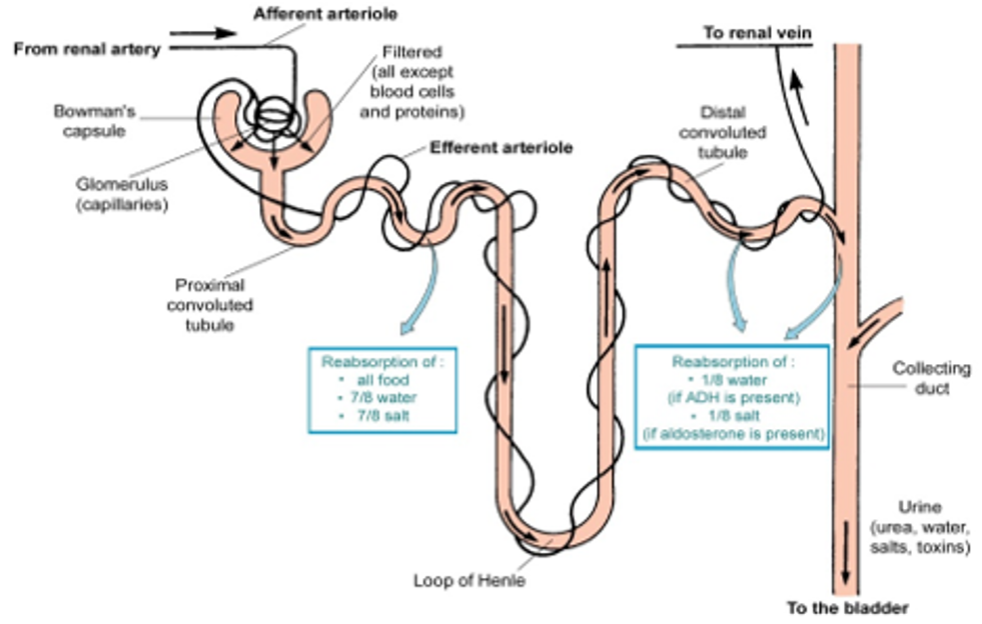
A nephron makes urine as follows
Filtration:
- blood enters the nephron in the afferent arteriole
- this forms many capillaries called the glomerulus
- high pressure in the glomerulus forces water and small molecules out of the blood
- glomerular filtrate is a dilute solution of waste and useful molecules
Reabsorption takes place in the following parts of the nephron:
- proximal tubule = water by osmosis, useful molecules and most salts by diffusion and active transport
- loop of Henle
- descending limb = water by osmosis
- ascending limb = salts by diffusion and then by active transport
- distal tubule = water by osmosis and some salts by active transport
- collecting ducts = water by osmosis
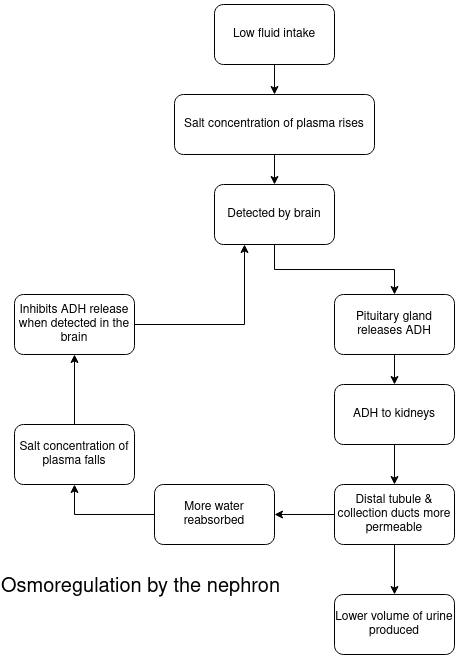
ADH and the Control of Water Loss (Osmoregulation) by the Nephron
ADH = Anti-diuretic Hormone
The permeability of the collecting duct wall to water is controlled by the hormone ADH (anti-diuretic hormone) made in the pituitary gland in the brain
If a lot of salt has been consumed or a lot of water has been lost by the body (eg. in sweat), the blood becomes too concentrated and water needs to be added to it
Osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus of the brain are stimulated and a message is sent to the pituitary to release more ADH into the blood
This causes the walls of the collecting duct to become more permeable to water and so more water leaves the collecting duct and goes into the blood. The urine remaining now has a smaller volume and is more concentrated
Drinking a lot of water results in less ADH being released, the walls remaining impermeable to water and therefore water remaining in the collecting duct. A watery urine of greater volume results