Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Selectively Permeable Membrane
- Phospho-lipid Bilayers
- Only allow certain substances in and out
- Occur as cell membrane & Nuclear membrane
Three Methods
1. Diffusion
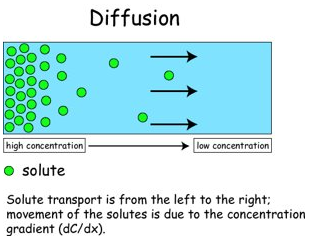
Diffusion is the movement of molecules (liquid or gas) from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
Diffusion is a passive process, requiring no energy
Examples of Diffusion:
- Smell of perfume
- A stink bomb!!
- Oxygen diffusing from the blood into the alveoli and carbon dioxide diffusing out of alveoli into blood-
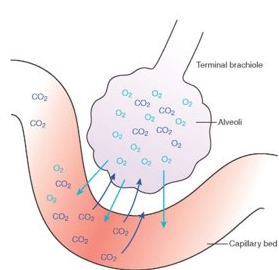
2. Osmosis
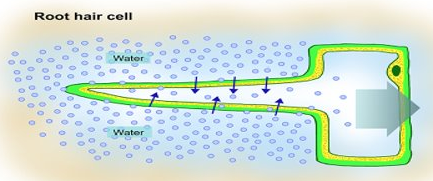
Osmosis is the movement of water from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration across a semi-permeable membrane
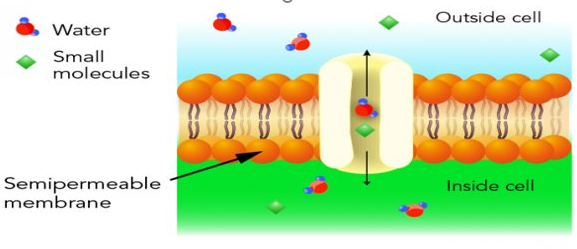
Osmosis is a passive process and does not require energy
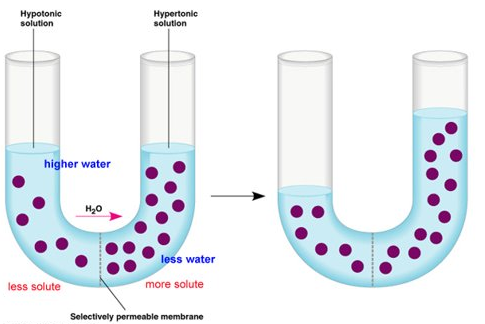
Solute is a substance that dissolves in a solvent e.g. salt, sugar
Concentrations
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
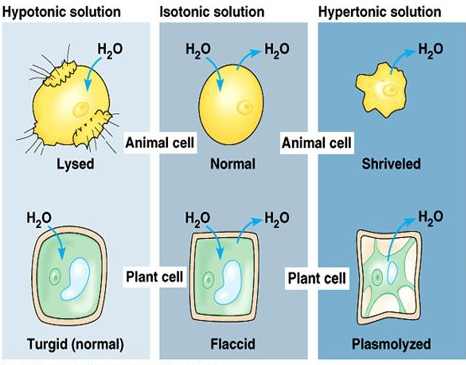
| Hypertonic | A solution that has a higher concentration (has less water) |
| Hypotonic | A solution that has a lower concentration (has more water) |
| Isotonic | Describes two solutions that have the same concentration |
Osmosis Terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
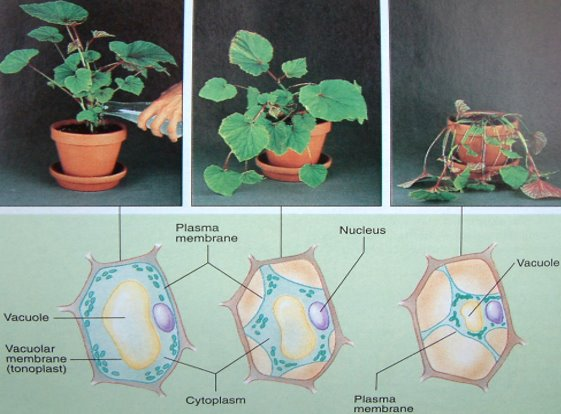
| Turgid | Cell that is firm because it is full of water (cell wall allows a plant to remain turgid for long periods of time) |
| Turgor | Benefits plants by keeping them upright and standing tall |
| Flaccid | A cell that is floppy because it lacks water - plant eventually wilts |
| Lysis | Bursting of a cell due to the intake of excess water |
Artificial semi-premeable membranes
Visking tubing and cellophane are artifical semi-premeable membranes and can be used to demonstrate osmosis

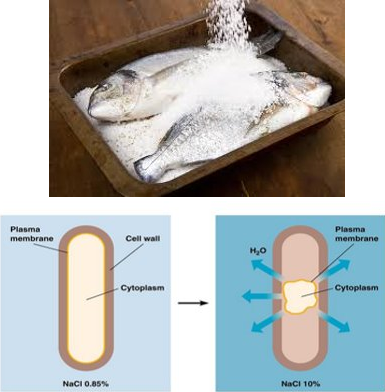
Food Preservation
Food spoilage is caused by bacteria
To avoid food spoilage:
- Food can be placed in a high solute concentration e.g. sugar or salt solution
- This causes the water inside the food cells and inside the bacteria to leave due to osmosis
- This dehydration means the bacteria cannot function
Examples of Food Preservation
3. Active Transport
**Active Transport** - The movement of **molecules** across a cell membrane **against** the concentration gradient i.e. from low concentration to high concentration
This process is active and requires energy
Cells involved in active transport have high energy requirements and contain many mitochondria
Example of Active Transport:
- Uptake of glucose in villi of small intestine