8. Management Activities: Planning, Organising and Controlling
Learning Outcomes from this chapter
On completion, you should be able to:
- Evaluate the effectiveness of the different management activities
- Analyse how different types of planning activities contribute to business success
- Define what a SWOT analysis is and illustrate it for a business
- Outline the features, benefits and challenges of different organisational structures
- Outline the situation in which different spans of controls are appropriate
- Describe how good management control systems can achieve efficiency in business
- Explain the methods a business could consider using to minimise the risk of bad debts
Definition of planning
Planning is when a business sets specific goals and objectives and then outlines strategies that allow it to achieve them
SWOT analysis: strengths/weaknesses (internal), opportunities/threats (external)
| S | Resources (e.g. patent, USP, design) |
| W | Outside chance (e.g. new market) |
| O | No website |
| T | Negative outside (e.g. new competitor) |
Strengths
- Products
- USP
- Good reputation
- High quality
Weakness
- Production issues
- Delivery delays
- Customer feedback
- Staff issues
Opportunities
- New market
- Legislation
- New supplier
Threats
- Taxation
- New competitors
- Weather
Steps in planning
- Analyse current situation
- Carry out a SWOT analysis
- Set goals/objectives
- Time related
- What we hope to achieve
- How we will achieve it
- Create a plan
- Labour (manpower) plan
- Resources planned out
- Strategic, tactical, contingency, operational
- Create the timeline
- When does each goal/objective need to be achieved
- Review the plan
- Check progress regularly
Types of planning
| Mission statement | Visionary statement containing the company values |
| Strategic planning | Created by senior management, long-term goals (from mission statement) |
| Tactical planning | Created by middle management, short-term goals (from strategic planning) |
| Operational planning | Day-to-day planning, staff rosters, etc. |
| Contingency planning | Back-up plan for an emergency or unforeseen event |
Benefits of planning
| Future-focused | Business can arrange resources effectively and be proactive |
| Reduces uncertainty | Plans for unforeseen events, clear objectives to follow |
| Attracts investors | Shows diligence, impresses investors, shows expected profits |
| Assesses performance | Checks objectives against actual performance; takes corrective action |
Organising
Organising: Arranging the resources of a business into an organised structure in order to achieve its objectives
Important terms
| Chain of command | Hierarchy in business from senior management down to employees |
| Span of control | Number of subordinates who report to one manager. Wide or narrow span, depending on factors such as: skills of the manager and workers, nature of work being done, company culture |
Chain of Command
- Armed forces
- Flows down (instructions)
Span of control
Factors affecting span of control:
- Skill of the manager
- Skill of the workforce
- Nature of the work
Organisational structures – functional
Benefits: specialisation, clear hierarchy, clear promotional path, wider span of control
Challenges: isolation of departments, hard to co-ordinate, communication issues across departments
Example of a functional organisation structure
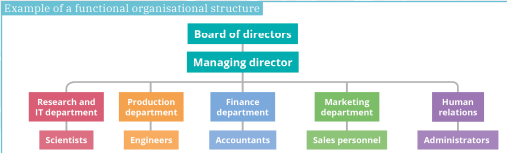
Organisational structures – matrix
Benefits: unity, improved decisions, relationships, responsibility
Challenges: slower decisions, unclear command, conflict
Example of a matrix organisation structure
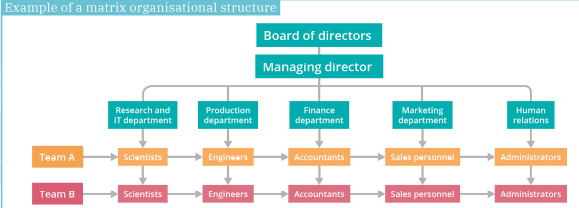
Organisational structures – product
Benefits: competition, focused resources, flexibility
Challenges: duplication, lack of cohesion, cannibalisation
Kerry Group’s corporate structure
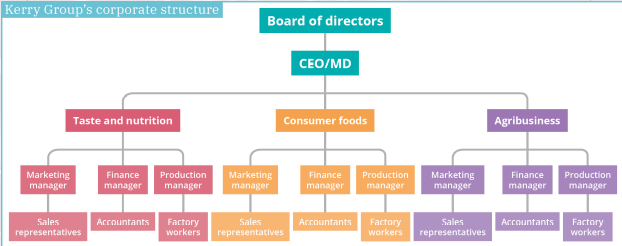
Organisational structures – geographical
Benefits: specialisation, clear hierarchy, clear promotional path, wider span of control
Challenges: isolation of departments, hard to co-ordinate, communication issues across departments
Starbucks’ geographical structure
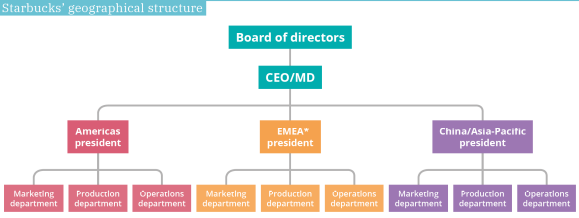
Controlling
Controlling: involves measuring any deviations away from a company’s plans and acting to correct them
The four areas of control for a business
| Financial control | Ensure profitability and liquidity. Plan (cash flow forecast), reduce costs (cheaper suppliers), ensure cash is available to pay short-term debts |
| Stock control | Achieve optimal stock levels (don’t under/overstock), reduce costs and obsolete goods, do regular stocktakes (check for theft), JIT |
| Quality control | Physical inspections (sampling), quality circles (staff teams), quality marks (ISO, Q Mark), improve consumer satisfaction/loyalty |
| Credit control | Minimise bad debts, incentivise cash payments, check creditworthiness of customers, set credit limits, penalise late payments, organise invoices |