6. Management Skills: Leading and Motivating
Learning Outcomes from This Chapter:
- Define the different management skills
- Outline the benefits of delegation for a business
- Explain the different leadership styles a manager could have
- Illustrate where different leadership styles may be more appropriate
- Discuss the main motivational theories used to motivate employees
- Outline the implications of adopting either a Theory X or Theory Y _
- Illustrate how a manager can satisfy the different levels of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Management Skill: Leading
A good leader can:
- Influence
- Delegate
- Directing
Leading: The ability to influence staff to follow strategies that meet the company’s aims, using directing and delegating
Managers are in charge of their employees and need to get their teams to perform tasks for the business. They might use directing
Directing: Guiding employees by issuing instructions, so they know how to carry out tasks and what to do
They may also use delegation
Delegation
Delegation: When a person in authority gives someone in a lower position in the business a task or project to complete, but the superior is still accountable and responsible for the task
Advantages of delegation
- Frees up the manager’s time to prioritise important tasks
- Shows trust in their staff, which can improve morale
- Staff improve skills and learn to handle responsibility
Implications of not delegating
- Manager may become overloaded with work
- Decision-making may be slowed
- Employees may be less capable of stepping up to higher roles
- Morale and motivation of staff are lowered
Leadership Styles: Autocratic
- Wants to control all decision-making
- Does not delegate work to staff
- Does not consult staff when making decisions
- Uses fear, threats or money incentives to motivate staff
It can be useful in a crisis, when quick decisions are needed
How does it help manage change?
It may help to manage change in the short term, but morale may suffer over a longer time period
Leadership Styles: Democratic
- Seeks opinions and feedback from staff when making decisions
- Delegates work to subordinates
- Results in staff feeling more valued and trusted
It is useful for most businesses as it creates teams and an inclusive environment where staff feel valued
How does it help manage change?
When change is implemented after a consultative process, staff feel more involved and included; this creates buy-in
Leadership Styles: Laissez-faire
- Sets deadlines and allows staff to decide how to achieve them
- Trusts staff to work without much supervision
- Allows staff to work without much interference
- Encourages intrapreneurship
- Frees up their own time for management
It may be useful with very skilled staff and in R&D
How does it help manage change?
Ownership of change is given to staff. This can motivate them
Motivation
Workers must be motivated to find their work interesting
Management need to develop good morale in the workplace
Motivating
High morale will exist in a firm when
- Employees receive satisfaction from what they do
- Employees take pride in their work
- Employees cooperate with and respect colleagues and superiors
- Employees feel that they are part of the team and that they make the business a success
Non Financial Motivation
Some people are motivated to work by more than just money
The following are some of the non financial factors that motivate people
- Security of employment
- Status (how you are seen to the public e.g. Doctor)
- Aspiration (desire to be promoted)
- Praise
Job Enlargement
Employees are given extra duties to do in order to relieve the boredom of work. These duties do not carry any extra responsibility
Disadvantages:
- Too much work
- Take too long
- Taken advantage of
- Decrease morale
Job Enrichment
Employees are given extra responsibility in the business. These tasks get them to develop their full abilities and skills
Disadvantages:
- Too muck work
- Take too long
- Costs more money
- Decreases morale (for those not picked)
- Competition in workforce
Improved working conditions
The employer may be flexible about what time the employees start and finish work. This is called flexitime. Longer holidays are also a way to reward employees
Importance of Pay and Rewards
- Motivated employees work harder
- Attracts the best employees
Training and Development
There are two ways to train workers
- On the job training
- Off the job training
On the Job Training
This is teaching the employee the knowledge, skills and attitude needed to do the job well, while she is in the normal working situation. She learns by having a go and practicing the tasks involved with the job
Techniques used include Job Rotation - This is where the employee is trained gradually from one department to another in the business
Advantages:
- Problem solving
- Improving skills and knowledge
- Learn through doing
Disadvantages:
- Premises does not have proper equipment
- Inexperienced staff delivering training
- Risk of poor example
Off the Job Training
This is teaching the employee the knowledge, skills and attitude needed to do the job well, away for the normal working situation
Techniques used include evening classes, conferences, and so on
Advantages:
- Problem solving
- Improving skills and knowledge
- Networking - Meet new people in the same role
Disadvantages:
- Learn through theory
- Have to travel to another facility
- Inexperienced staff delivering training - Never worked in the role
Development
This is giving employees life-long skills and knowledge that will help them to grow as individuals
It is more than training. Development teaches an employee skills that they can use in any job
Communication Skills is an example of development
Importance of Training and Development
Gives the workers the skills needed to do a good job and better quality products as a result
↓
Makes workers more flexible and able to cope with changes
↓
Workers need less supervision
↓
Less conflict between workers and managers as workers are good at their jobs
Maslow’s Theory of Motivation
Maslow was a scientist who believed that people in organisations were motivated by a hierarchy of needs from low needs to high need
Low needs are essentials like food, shelter and safety must be met before high needs such as social acceptance or esteem can be satisfied
He believed that every person has the same needs
He referred to the following
- Every person has needs which must be satisfied. As a need is satisfied another need is the next motivating factor
- The needs are arranged in progressive levels - from low to high
- A person’s job can help to satisfy these needs
The different needs are called the hierarchy of needs and include the following
- Physiological needs (essential needs)
- Food, drink, clothes, wage
- Security needs
- Job security, employment contract, pension etc.
- Social needs
- Friends, social club membership
- Esteem needs
- Status - title, promotion
- Self actualisation needs
- Being ambitious, being given more responsibility in work, becoming an entrepreneur
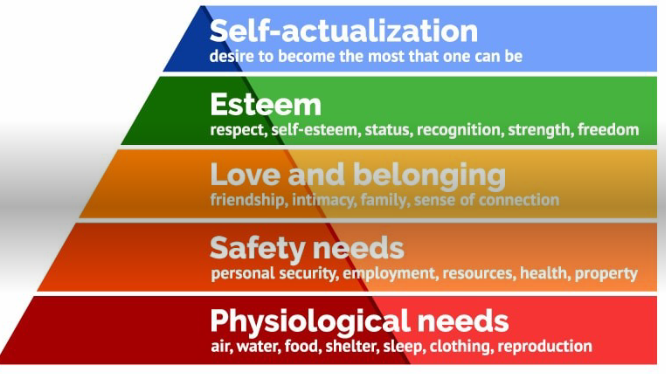
Problems with Maslow’s Theory
- Not everyone has needs in the same order
- (Some) Aren’t needs
- Solitary people aren’t considered
- Different psychology
- Disability
- Higher level of need not considered
Implications of Maslow’s Theory
Once financial needs are satisfied, additional rewards will be required in order to satisfy some higher needs
Employee’s attitudes and effort in work will be related to the success in management in satisfying their non financial needs
Morale will be low if the work is boring, regardless of the pay. A firm with low morale will have high absenteeism. Profits will also fall
McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y
McGregor was an American social psychologist and management consultant. He analysed the way in which employees and employers looked at work
Employer: Is the boss, pays the wages, gives instructions, doesn’t like unions
Employee: does the job, takes the wages, accepts no responsibility
While managing different firms he noticed two different styles of management. These became known as Theory X and Theory Y
Theory X (From Slides)
- Most employees are lazy and need to be supervised
- Management must offer incentives to motivate ‘lazy’ employees
- Most employees require safety and security needs as a priority
- Most employees lack ambition and need to be motivated to ‘pull their weight’
- Most employees will resist changes and are easily influenced by others
-
Theory X (From Teacher)
Autocratic style of management
- Not a good worker
- Motivated by only money
- Supervision required at all times
- Resist change
- Require safety & security needs
- Lack ambition
Theory Y (From Slides)
- Employees enjoy working and are willing to work and accept responsibility
- Employees are able to motivate themselves, strict supervision is not required
- Satisfying their self actualisation needs by giving them more responsibility is a very good way of getting them fully committed to their job
- All employees should receive training
- Workers skills are not always maximised
-
Theory Y (From Teacher)
Democratic style of management
- Supervision greatly reduced or gone, self motivated
- Works hard. enjoys working
- Motivated outside of money
- Self actualisation through responsibility
- *Receive training
- *Skills not maximised