Skeletal System
Syllabus Objective
- Description of the structure and functions of the skeleton
- Component parts of the axial skeleton: skull, vertebrae, ribs, and sternum
- Position and function of discs in relation to vertebrae
- Component parts of the appendicular skeleton: pectoral and pelvic girdles and their attached limbs
- Macroscopic anatomy of a long bone: medullary cavity, compact bone, spongy bone, and cartilage
- Function of the following: cartilage, compact bone, spongy bone (include red and yellow marrows)
- Classification, location and function of joints: immovable, slightly movable, free-moving or synovial
- Role of cartilage and ligaments in joints
- Role of tendons
- General relation of muscles to the skeleton – antagonistic muscle pairs as exemplified by one human pair
- Disorders of the musculoskeletal system: one example of a musculoskeletal disorder, from the following: arthritis and osteoporosis; one possible cause, prevention, and treatment
- Osteoblast role in bone growth. Terminating development of adult height. Role of osteoblasts in bone cell replacement. Bone renewal. Role of calcium in bone
Description of the structure and functions of the skeleton
The skeleton contains 206 bones and can be divided into an axial and appendicular skeleton. It provides support, protection and allows movement
Functions of the Skeleton
-
Support
The skeleton provides an internal framework that provides space for organs to develop
-
Protection (of major organs)
The skull protects the brain, the rib cage protects the lungs and heart but can move in and out to allow breathing.The vertebrae protect the spinal cord which runs through it
-
Movement
When muscles attached to bones contract they cause movement
-
Blood Cells
Blood cells are made in the bone marrow of the ribs, pelvis and sternum
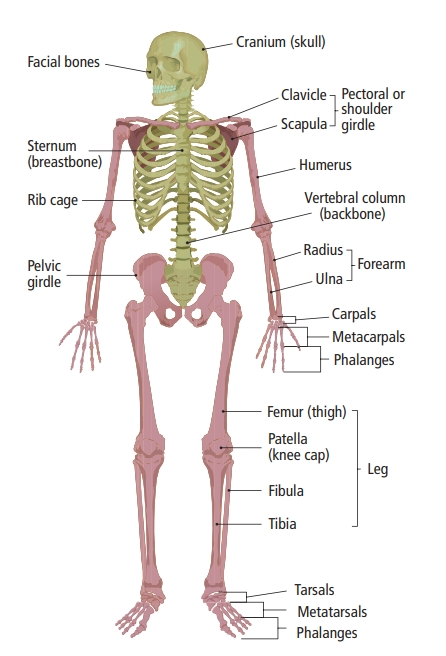
Component parts of the axial skeleton: skull, vertebrae, ribs, and sternum. Position and function of discs in relation to vertebrae
The axial skeleton consists of the skull, vertebrae, ribs and sternum
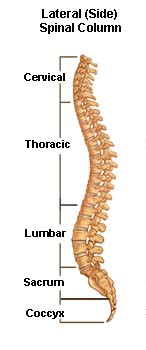
The back consists of 33 vertebrae bones
- *7 cervical vertebrae are in the neck
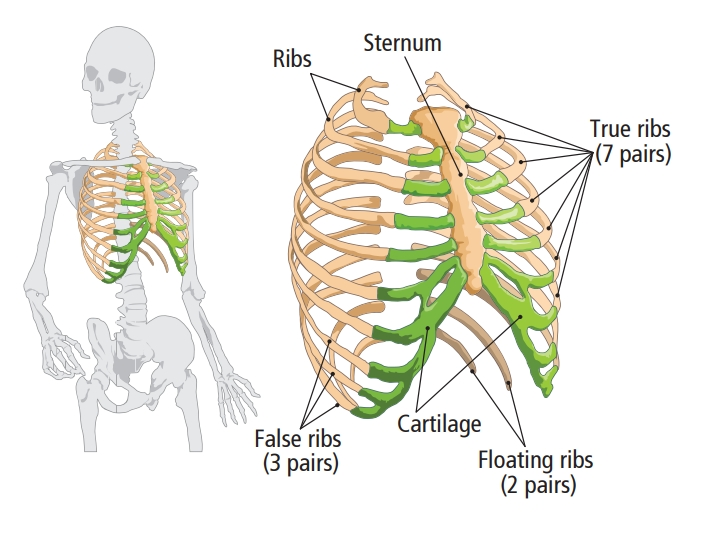
- *12 thoracic vertebrae in the upper back attached to each of 12 pairs of ribs.
- 5 lumbar vertebrae in the lower back
- 5 fused sacral vertebra
- 3 small vertebrae in the coccyx
Discs of cartilage are found in between the vertebrae and act as shock absorbers
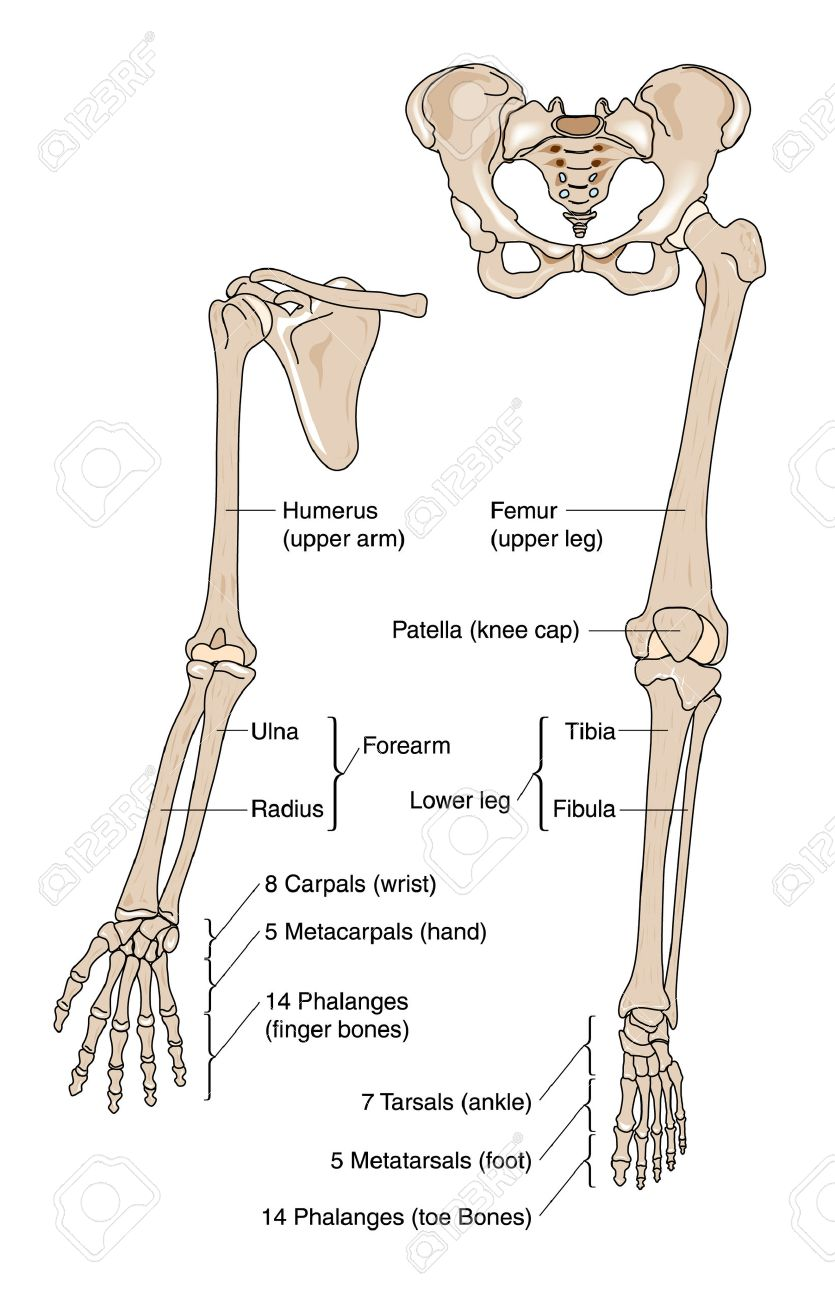
Component parts of the appendicular skeleton: pectoral and pelvic girdles and their attached limbs
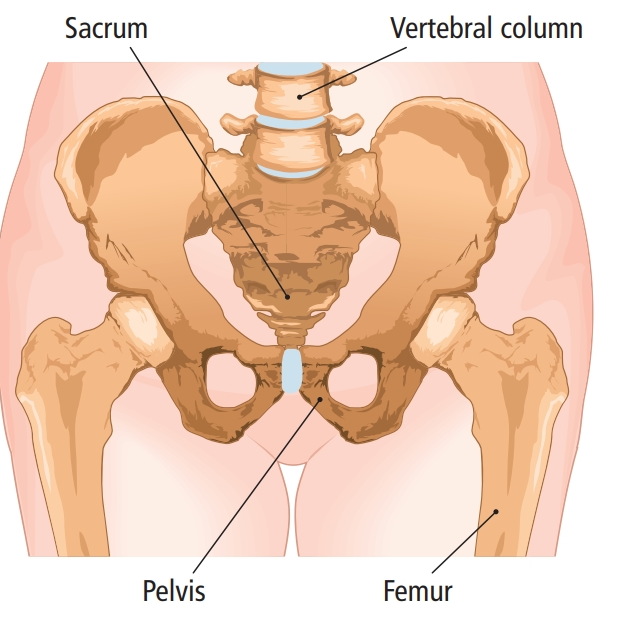
The appendicular skeleton consists of the pelvic girdle (hips), the pectoral girdle (shoulders), the scapula, clavicle (collar bone) and the bones of the arms and legs
Arms Bones
Humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges
Leg Bones
Femur, tibia, fibula, tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges
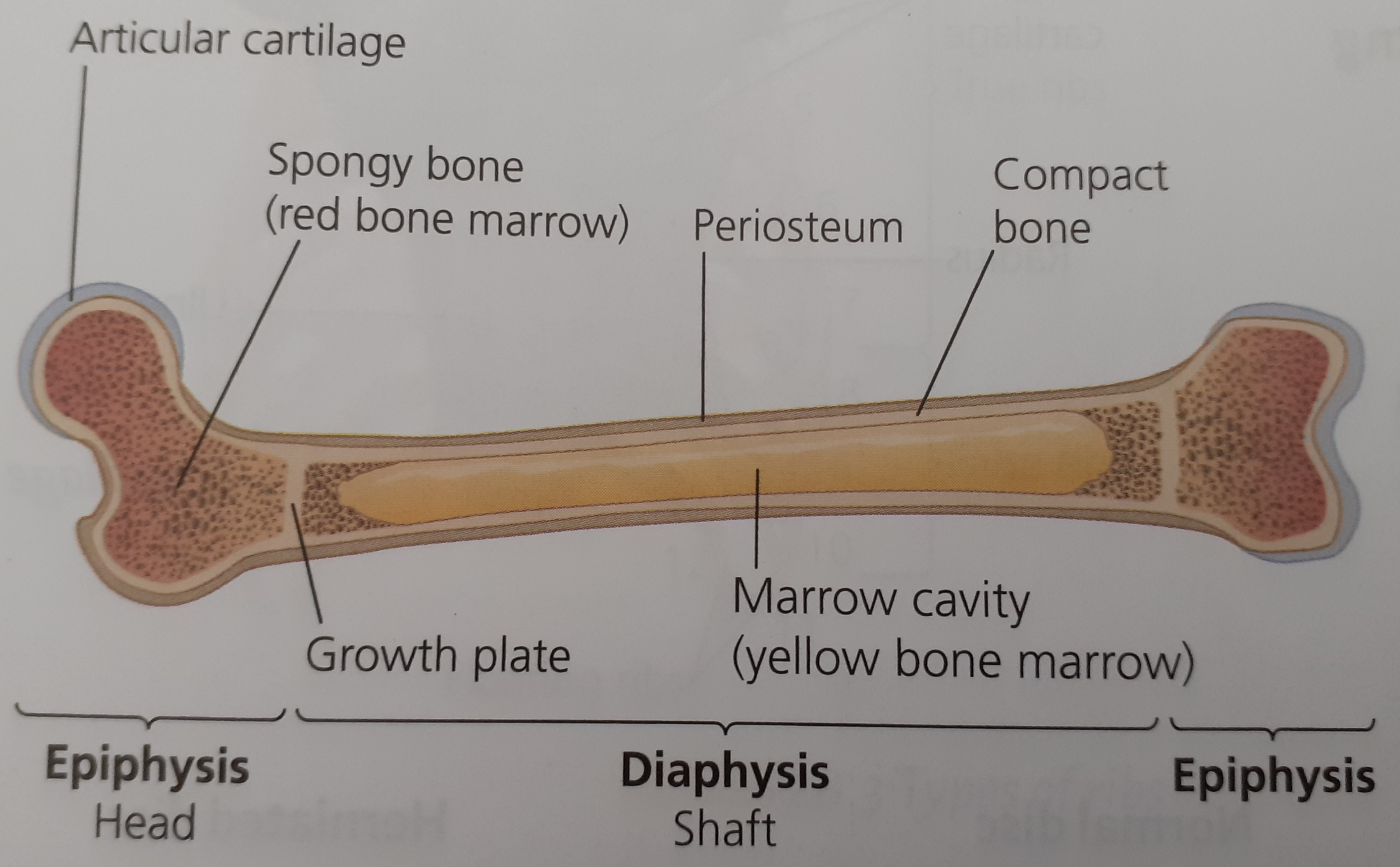
Macroscopic anatomy of a long bone: medullary cavity, compact bone, spongy bone, and cartilage.
Function of the following: cartilage, compact bone, spongy bone (include red and yellow marrows
Bone is mixture of organic material -protein and inorganic material calcium phosphate. The periosteum is a thin layer of connective tissue that covers the outer surface of bone.
Compact bone found in the shaft of long bones is dense with very few gaps provides support and protection
Spongy bone found in the heads of long bones is low density with spaces often filled with bone marrow
Medullary cavity
Bone marrow is found in the medullary cavity of long bones. Yellow bone marrow acts as a store of fat, red bone marrow produces blood cells
Cartilage at the ends of long bones act as shock absorbers and reduce friction at joints
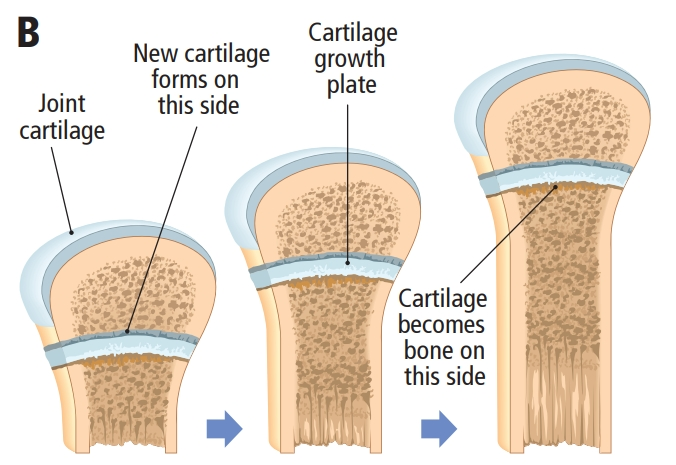
Osteoblast role in bone growth. Terminating development of adult height. Role of osteoblasts in bone cell replacement. Bone renewal. Role of calcium in bone
Bone is constantly broken down and replaced by cells called Osteocytes which remove calcium removing excess bone and osteoblasts lay calcium down building bone
Continued renewal of bones depends on calcium in the diet, exercise and is affected by parathormone levels in the blood
During growth osteoblasts produce a layer of bone around the cartilage growth plate between the diaphyses and epiphyses. The growth plates allows the bones to elongate during childhood and puberty and eventually calcify and turn completely to bone at the end of puberty
Osteocytes and osteoblasts
- Osteocytes are cells that dissolve bones
- Osteoblasts are cells that form new bones
Classification, location and function of joints: immovable, slightly movable, free-moving or synovial. Role of cartilage and ligaments in joints. Role of tendons
A joint is where 2 bones meet
Immovable Joints
The skull consists of a number of bone plates fused together
Slightly movable Joints
Vertebrae can move a little providing limited flexibility
Free-moving Joints
The elbow and knee are examples of hinge joints; the hip and shoulder are ball and socket joints. Synovial fluid lubricates the joint. Cartilage act as shock absorbers and prevents bones rubbing against each other causing pain
Tendons attach bone to muscle
Ligaments attach bone to bone
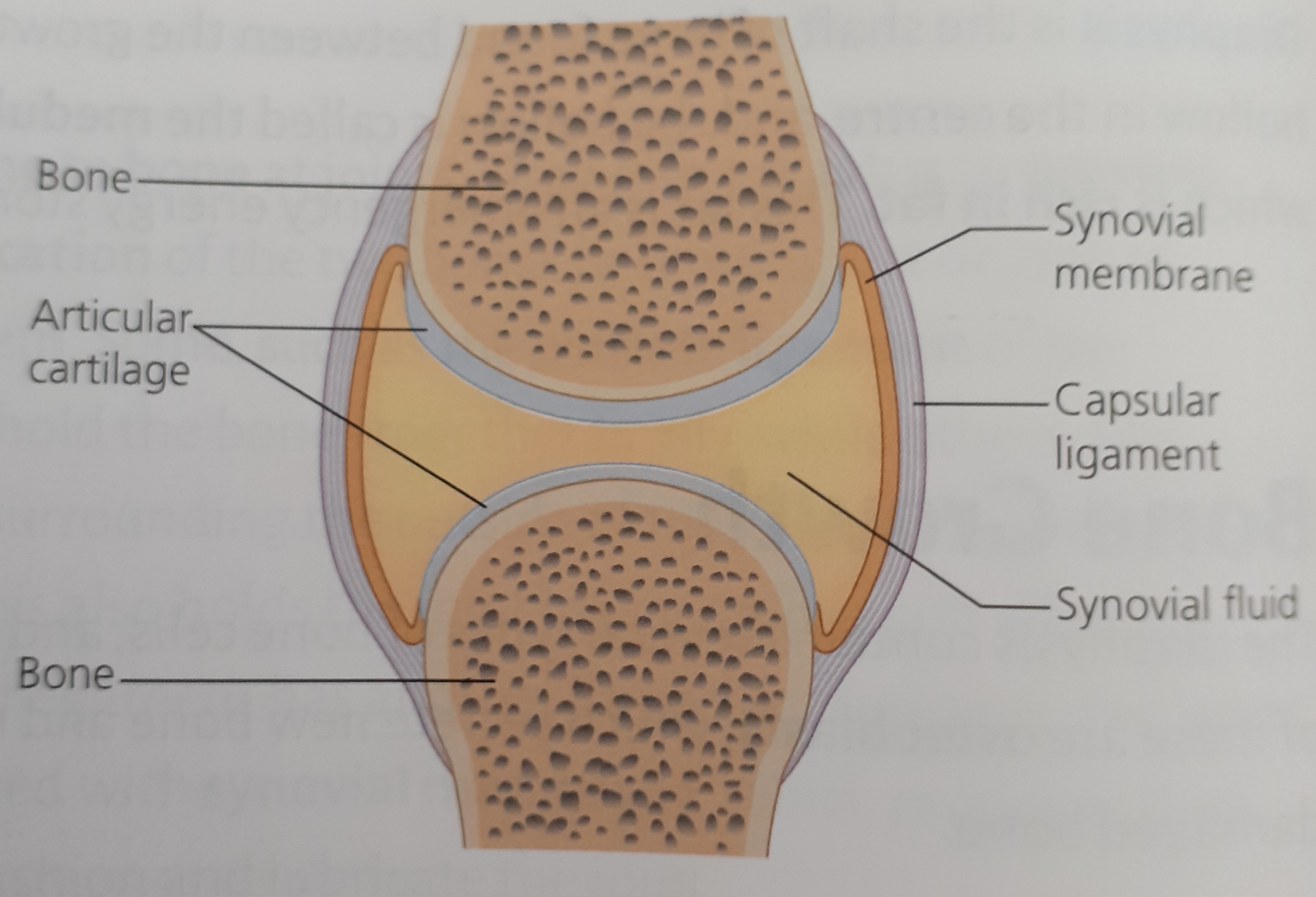
Synovial membrane makes synovial fluid
- Hinge joints move in one plane only
- Example: elbow
- Ball & Socket Joints can move in all planes
- Example: shoulder
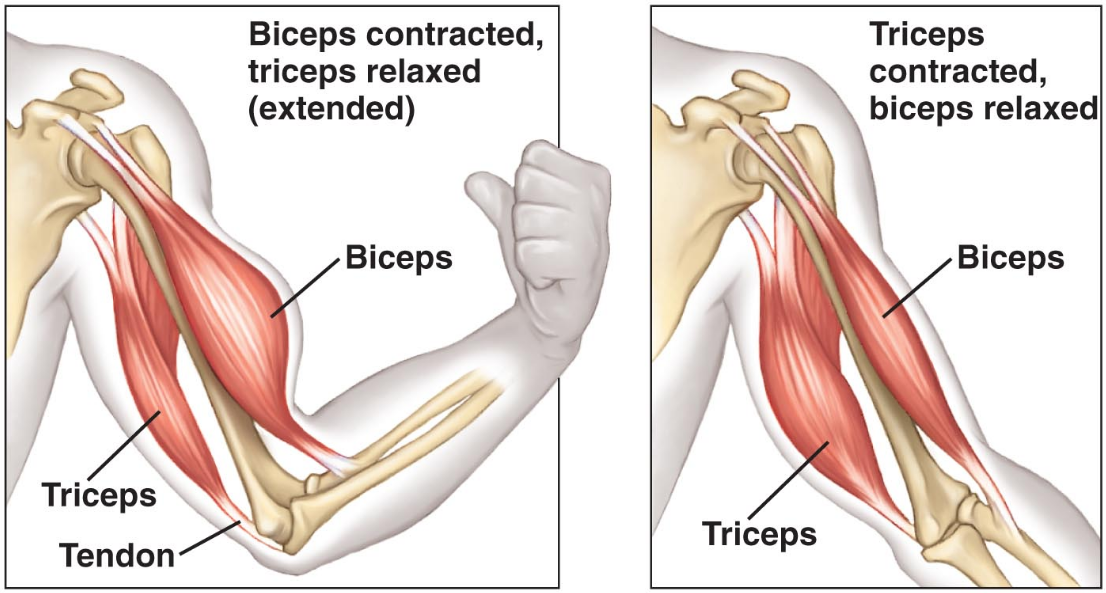
General relation of muscles to the skeleton – antagonistic muscle pairs as exemplified by one human pair
Muscle is contractile tissue that has the ability to shorten and generate a pulling force
Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles as they can be consciously controlled
Antagonistic muscles work opposite each other in pairs
Example: the biceps and triceps
The biceps contracts and the triceps relax to raise the lower arm
The triceps contracts and the biceps relax to lower the lower arm
As one contracts the other must relax
Biceps and Triceps, Raising and Lowering
| Muscles | Raising | Lowering |
|---|---|---|
| Biceps | Contract | Relaxs |
| Triceps | Relaxs | Contracts |
Disorders of the musculoskeletal system: one example of a musculoskeletal disorder, from the following: arthritis and osteoporosis; one possible cause, prevention, and treatment
Arthritis
Arthritis is inflammation or swelling that affects the joints and can limit movement of the joint and cause pain
Cause
It can be caused by wear and tear of the joint during manual work or can be caused if the white blood cells of the body attack the cartilage of the joint
Prevention
Maintaining a healthy weight may limit the effects of arthritis. No known preventative measure yet
Treatment
It can be treated with anti-inflammatory painkillers and artificial joint replacement
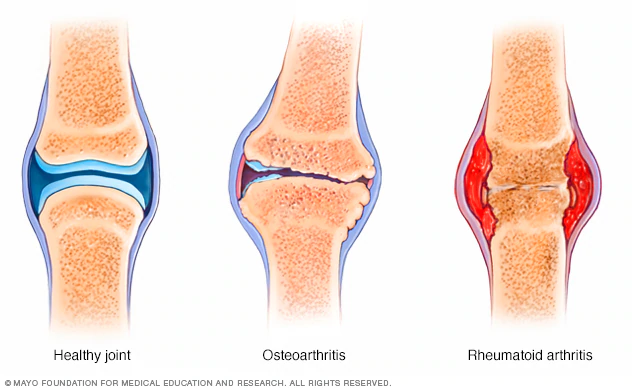
The main difference between osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis is the cause behind the joint symptoms. Osteoarthritis is caused by mechanical wear and tear on joints. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s own immune system attacks the body’s joints