Circulatory System
All larger organisms require a transport (vascular) system to bring food and oxygen to the cells and to remove waste
Humans have a closed circulatory system - blood circulates inside closed vessels (insects have an open system - open ended vessels). Blood can travel much faster in a closed system
Blood Vessels - 3 Types
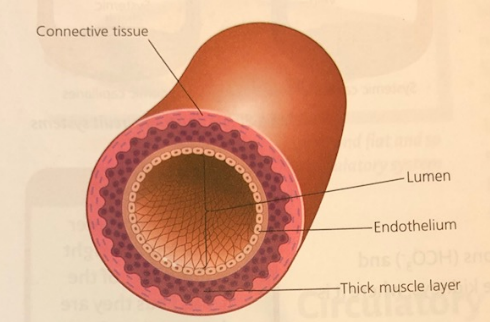
- Arteries
- Brings blood down away from heart under high pressure
- Have no valves to stop backflow
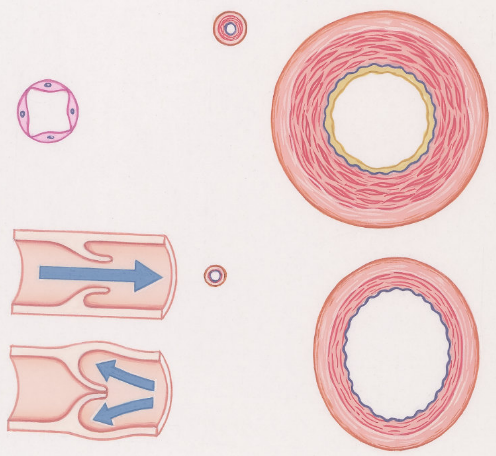
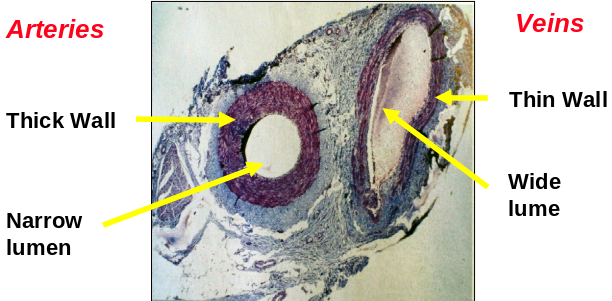
- Thick walls to cope with high pressure
- Narrow lumen (space inside)
- Arteries carry oxygenated (high in oxygen, low in carbon dioxide) blood (except pulmonary artery)
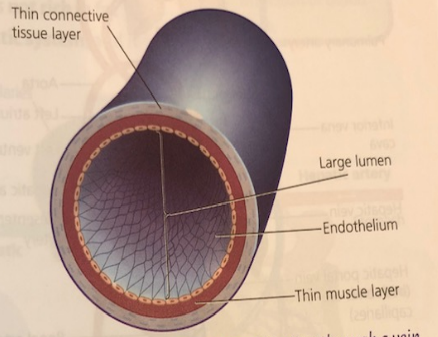
- Veins
- Brings blood to heart under lower pressure
- Veins have valves to prevent backflow of blood
- Veins have thinner walls
- Veins have a larger lumen (space inside)
- Veins carry deoxygenated (low in oxygen, high in carbon dioxide) blood (except for pulmonary vein)
- Capillaries
- Thin wall - 1 cell thick
- Tiny blood vessels
- They allow materials to be exchanged between the blood and cells e.g. oxygen
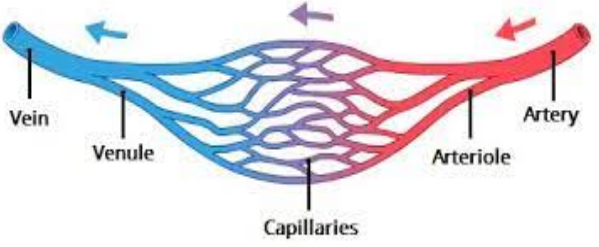
Smaller Blood Vessels
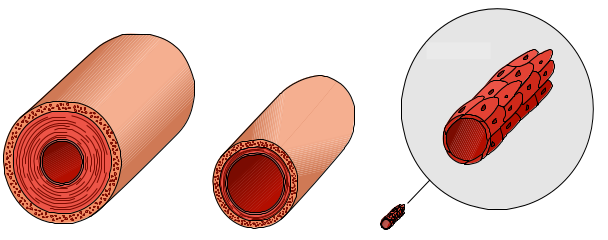
Arterioles
- Arterioles connect arteries and capillaries
Venules
- Venules connect capillaries to the veins
Capillaries
- Tiny blood vessels linking arterioles and venules
- The thin wall allows easy exchange of materials with cells
Comparison of vessels
Blood Vessels Under the Microscope
Blood
- 55% liquid called plasma (yellow in colour)
- 45% cellular componenets
Three Functions of Blood
- Transport
- Temperature regulation
- Defence against disease
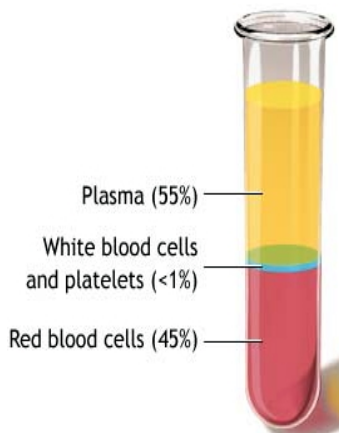
Blood is made up of 4 parts
- Plasma
- Red Blood Cells
- White Blood Cells
- Platelets
Plasma
- Transport of substances such as glucose, amino acids, vitamins
- Helps keep body at optimum body temperature by transferring heat
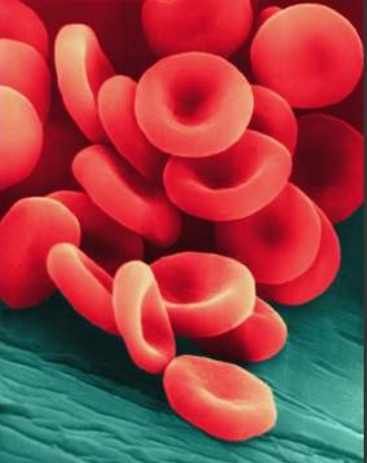
Red Blood Cells (rbc)
- Biconcave Discs
- No nucleus (prokaryote)
- No mitochondria
- Flexible membrane
- Made continuously in red bone marrow of ribs and sternum
- Contain the red coloured iron containing hemoglobin which carry oxygen
- Anaemia - disease where blood lacks enough red blood cells to carry oxygen efficiently causing excess tiredness
- Caused by lack of iron in diet, can also be a genetic disorder
White Blood Cells (wbc)
- Larger and less of them then red blood cells
- Have a nucleus (eukaryote)
- Protect body against disease
2 Types
- Monocytes = Engulf bacteria by phagocytosis
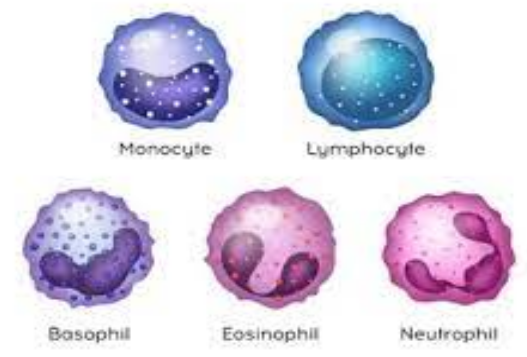
- Lymphocytes = Made in lymphatic system. They form antibodies, which are chemicals used to kill bacteria and viruses (More of these)
Platelets
- Fragments of larger cells formed in bone marrow
- Important role in clotting the blood (scab)
Blood Grouping Systems
- ABO system = There are 4 blood groups: A, B, AB and O. O is the universal donor and AB is the universal recipient
- Rhesus system = Humans are rhesus positive or rhesus negative. If a baby is Rh+ and its mother is Rh-, it can cause complications during pregnancy and childbirth
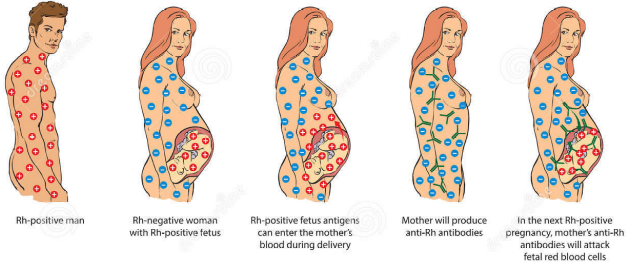
Anti D = injection which removes babys Rh + blood that has entered mothers system
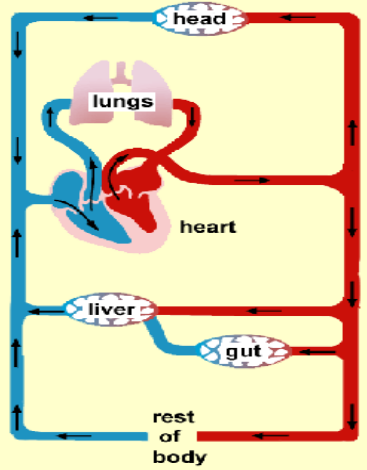
Double Circulation in Humans
The human circulatory system is a two-circuit system:
- Pulmonary Circuit
- Heart → Lungs → Heart
- Systemic Circuit
- Heart → Body → Heart
Double Circulation
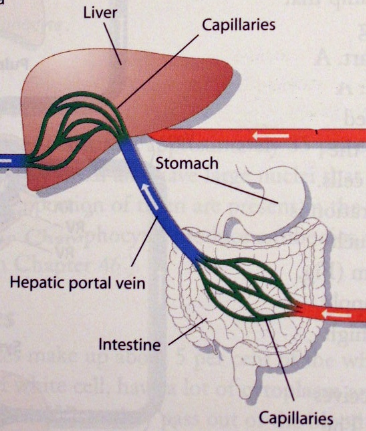
Portal Systems
A portal system carries blood directly from one organ to another without going through the heart
E.g. Hepatic Portal System
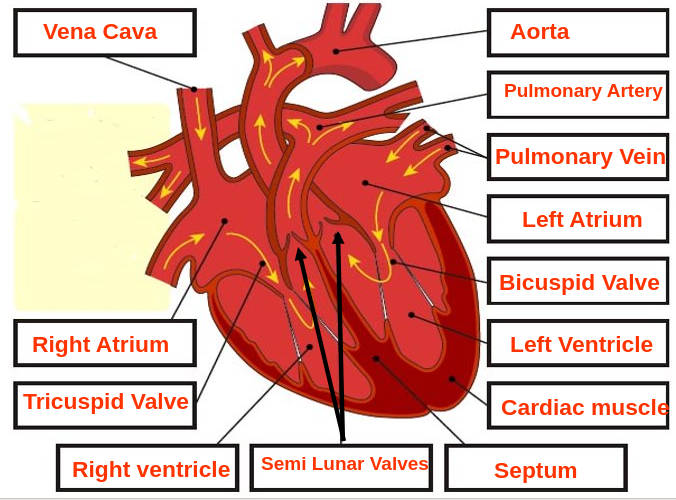
The Heart ♡
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Location | Between the lungs, slightly to the left side of the thorax, above the diaphragm |
| Function | To pump blood around the body (has its own blood supply through coronary artery) |
| Structure | A hollow structure made of cardiac muscle, surrounded by a double membrane |
Role of Heart Muscle
- The heart wall is made of Cardiac Muscle
- Contraction of the cardiac muscle drives blood around the body
- Cardiac Muscle does not fatigue (tire easily) because it has it’s own blood supply (coronary artery)
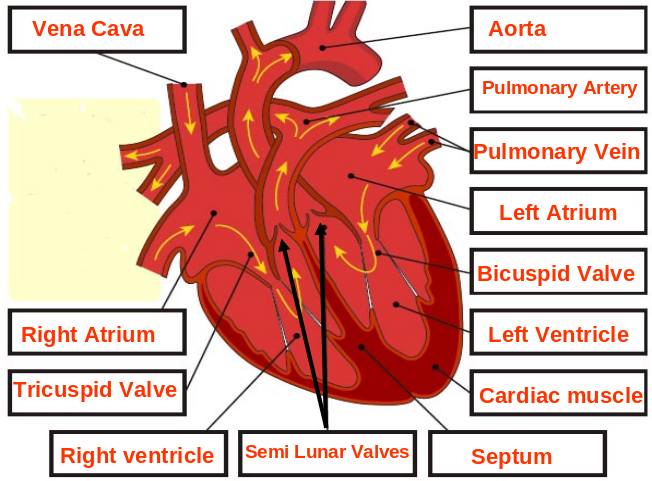
Blood pathway through heart
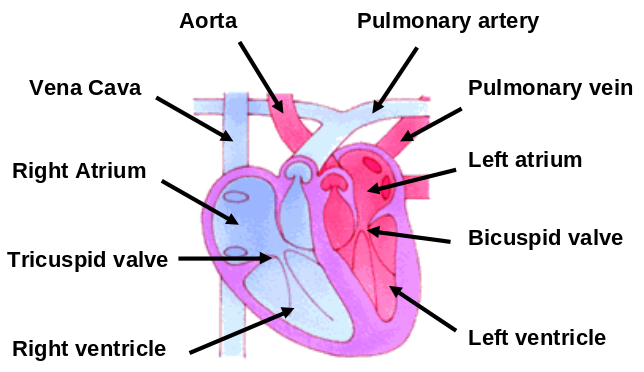
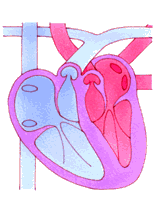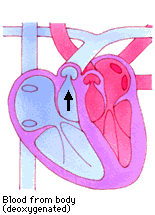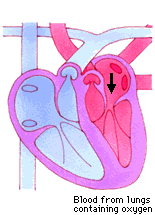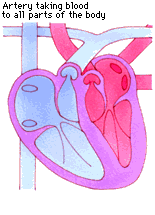
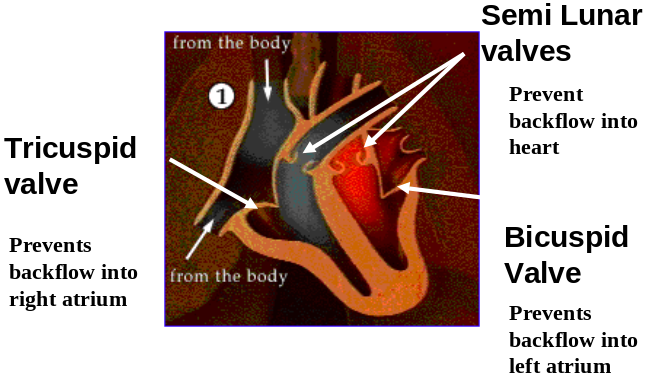
Roles of Valves
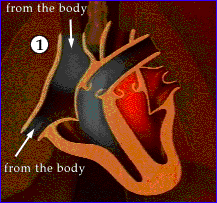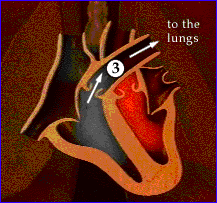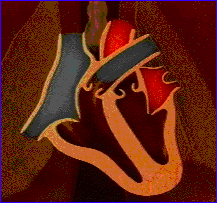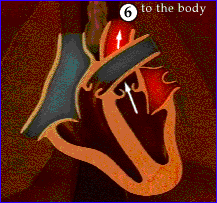
Blood supply to the heart wall
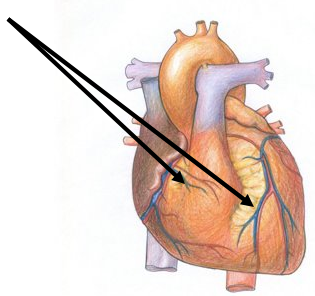
(Arrows are supposed to be labelled Coronary Arteries)
Coronary Arteries
Cardiam muscle is supplied with blood by the coronary arteries. These branch from the aorta just above the semi lunar vavles of the aorta
Coronary Veins
Drain blood from heart wall into the wall atrium
Heartbeat and its control
- The heart beat consists of alternate contraction and relaxation of the cardiac muscle
- The heart beat is controlled by the pacemaker in the right atrium. This sends an electrical signal to the cardiac muscle
- The heart beat sound is caused by the closing of the heart valves
Heartbeat Control (Need to Know)
- The location of the SA and AV nodes
- Distinguish between Systole & Diastole
- Be aware that cardiac muscle in the heart wall is specialised not to fatigue
- Be able to describe the sequence of events in the cardiac cycle
- Explain the role of the SA and AV nodes in systole and diastole
Factors affecting Heart Rate
Heart rate is increased by
- Exercise
- Stress
Heart rate is decreased by
- Sleep
- Alcohol
Heart Rate Control
Controlled by the Pacemaker (SA (sino atrial) Node) in the right atrium wall
The SA Node emits an electrical signal
This causes the atria to contract
This signal is picked up by the AV (atrioventricular) node
The AV node sends a signal to the ventricles
Causing the ventricles to contract
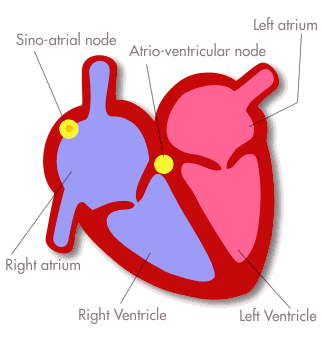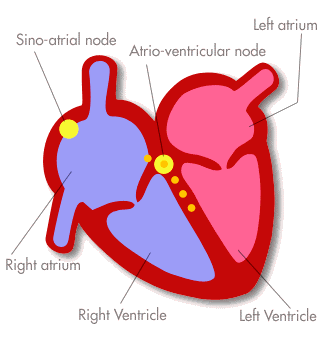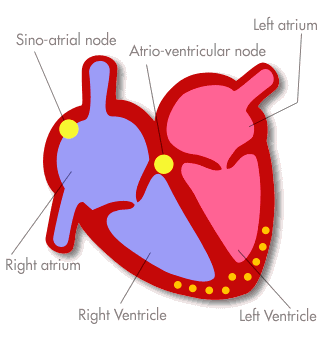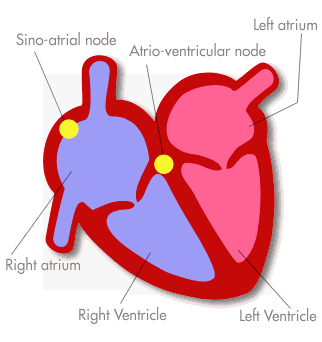
Stages of the Heartbeat
Contraction of heart muscle is called SYSTOLE
Relaxation of heart muscle is called DIASTOLE
-
Blood enters the two atria. All valves are closed
All chambers are relaxed (diastole)
- The atria contract (systole), tricuspid and bicuspid valves open, blood is forced down into ventricles
- Atria relax (diastole), ventricles contract (systole), Bicuspid and tricuspid valves close, semi lunar valves open and blood is forced into the pulmonary artery and aorta
-
Ventricles relax (diastole), semi lunar valves close.
The cycle starts again
Pulse
The alternate expansion and contraction of arteries is called a pulse
Average pulse rate is 72 beats per minute
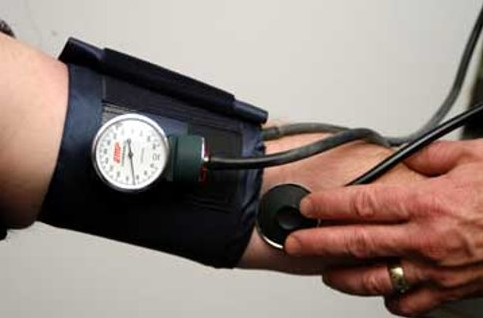
Blood Pressure
Pressure in blood due to the contraction of the ventricles which forces blood into the arteries
Blood pressure is measured with an instrument that records the pressure it takes to stop the blood flow in an artery of the upper arm
Effect of Smoking on the Circulation System

-
Nicotine increases the heart rate and blood pressure
These puts a bigger workload on the heart
-
CO2 reduces the amount of O2 carried bu the blood
This reduces energy levels
-
Other chemicals in tobacco
Increase the chance of clots
Effect of Diet on the Circulation System

High intake of fat causes a build up of cholesterol
Cholesterol may block arterioles and lead to stroke or heart attack
High salt intake raises blood pressure which can cause a heart attack
Effect of Exercise on the Circulation System

Exercise strengthens the heart
This improves circulation
Exercise increases our ability to transport oxygen
This gives increased energy levels
Lymphatic System
A secondary transport system consisting of one way system of vessels that collects and return excess tissue fluid to blood system
Structure:
- Lymph Vessels
- Lymph Nodes
- Lymph
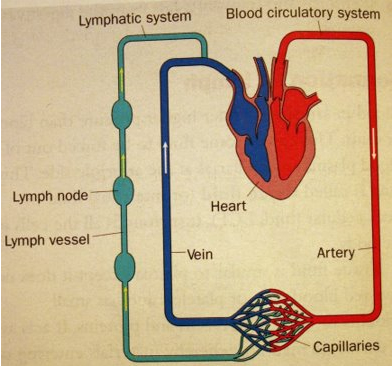
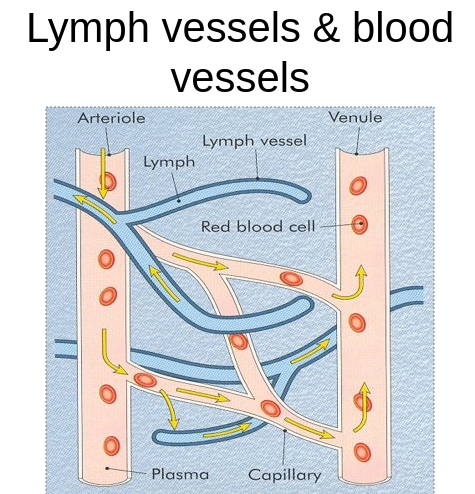
10% of tissue fluid enters the lymphatic system
Lymphatic System Functions
- Collect tissue fluid and return it to the blood system
- Fight infection by
- Filtering out microorganisms in the lymph nodes
- Destroying microorganisms by antibody production
- Mature and store lymphocytes
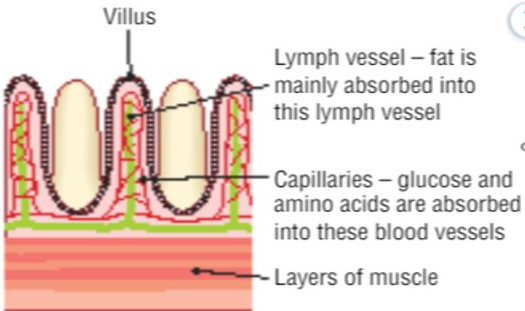
- Transport digested fat away from intestine
Flashcards (From Teacher)
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| State one factor that increase heart rate | Fear (fright) OR exercise |
| Where in your dissection did you find the origin of the coronary artery? | Aorta OR near semilunar valve |
| State a possible effect of smoking on the pulse resting rate | Raises rate |
| State a precise location in the human body at which red blood cells are made | Marrow OR named bone, e.g. skull/ribs/vertebrae/sternum |
| Name the liquid part of blood | Plasma |
| Name two tissues that are present in the walls of arteries and veins | Epithelial OR connective OR muscular (any two) |
| Name two common blood-grouping systems | ABO AND Rhesus |
| What structural protein, found in the walls of arteries, is non-elastic and prevents over expansion of the vessels? | Collagen |
| What is the function of a semilunar valve? | Stops back flow of blood into ventricle (or from artery) |
| State one factor that decreases heart rate | Sleep OR drugs (sedatives) |
| Why are valves not needed in arteries? | Blood is under pressure OR blood from heart OR blood pumped |
| Which chamber of the heart has the greatest amount of muscle in its wall? | Left ventricle |
| Name the chamber of the heart that receives blood back from the lungs | Left artium (auricle) |
| What is the role of the SA (sinoatrial) node in heart? | Causes contraction (of heart muscle) OR Pacemaker OR impulse generation |
| State one way in which heart muscle differs from other muscles in the body | Doesn’t tire |
| The human circulatory system has two circuits, the pulmonary and systemic. Which of these circuits involves the pumping of blood by the left ventricle? | Systemic (circuit) |
| Veins contain valves whereas arteries do not. What is the function of the valves? | Prevent backflow of blood |
| Blood contains red corpuscles and white cells. State one function the white cells. | Protection against disease |
| State on function of the liquid part of blood | Transports “cells” and dissolved substances |
| What is the average resting rate of the human heart in beats per minute? | 72 bpm |
| What is the role of the AV (atrioventricular) node in the heart? | Causes contraction (of heart muscle) OR nerve impulse generation |
| The hepatic portal vein carried blood from the alimentary canal to the … | Liver |
| Give the precise location of the AV node | In or near septum OR near tricuspid valve OR between atrium and ventricle |
| Name the valve between the upper and lower chambers on the left-hand side | Bicuspid (mitral) valve |
| The ABO blood group system has four blood groups. What are these four groups? | A, B, AB and O |
| Give on reason why the wall of the left ventricle is thicker than the wall of the right ventricle | Pumps further OR maintains blood pressure OR greater activity |
| Name the artery that supplies the heart muscle with blood | Coronary (artery) |
| Blood contains red corpuscles and white cells. State on function of the red corpuscles | Transports oxygen |
| What is the function of the bicuspid valve? | Prevent backflow of blood from left ventricle to left auricle (atrium) |
| To where does the pulmonary artery carry blood? | Lungs |
| How does a portal vein differ from other veins? | Capillaries at both ends OR joins two organs OR two named organs |
| Which has the bigger lumen (cavity), an artery or a vein? | Vein |
| Is the blood in the Aorta oxygenated or deoxygenated? | Oxygenated |
| What is blood plasma? | Blood without cells OR watery liquid part of blood |
| Name the upper chambers of the heart | Atria OR Auricles |
| What structure(s) protects the heart? | Rib cage and sternum |
| Name the blood vessel that brings blood from the heart to the body | Aorta |
| Name the cavity of the body in which the heart and lungs are located | Thoracic OR chest |
| The human circulatory system has two circuits. Give the name of each of these circuits | Pulmonary circuit and Systemic circuit |
| At the start of an investigation of the effect of exercise on the pulse rate of a human you ask the person who is about to do the exercise to sit down for a few minutes. Explain the purpose of this | Comparison OR control OR to get resting rate OR normal rate |