The Cell
The smallest unit of living matter
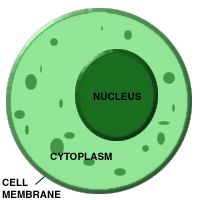
Animal & Plant Cells - Basic Structure
Animal Cells
- Cell Membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus
- Mitochondria
Only the cell membrane, the cytoplasm and the nucleus can be seen under the light microscope
Plant Cells
- Cell Membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus
- Cell Wall
- Chloroplast
- Large Vacuole
- Mitochondria
Cell Ultra-structure
The fine details of a cell’s structure can only be seen using an electron microscope
Cytoplasm is the watery liquid inside the cell membrane
Organelles are small structures found in the cytoplasm
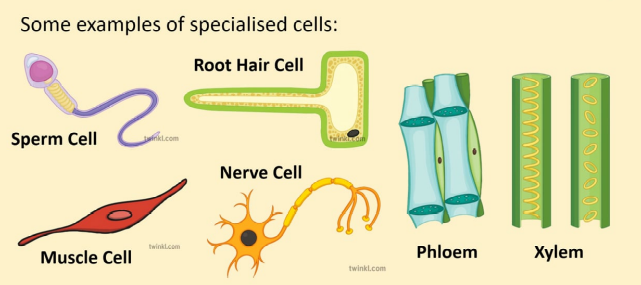
Animal Cell
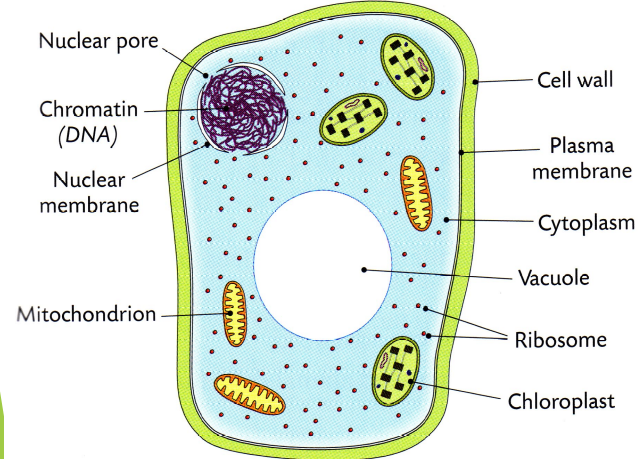
Animal Cell Ultra-Structure
Plant Cell
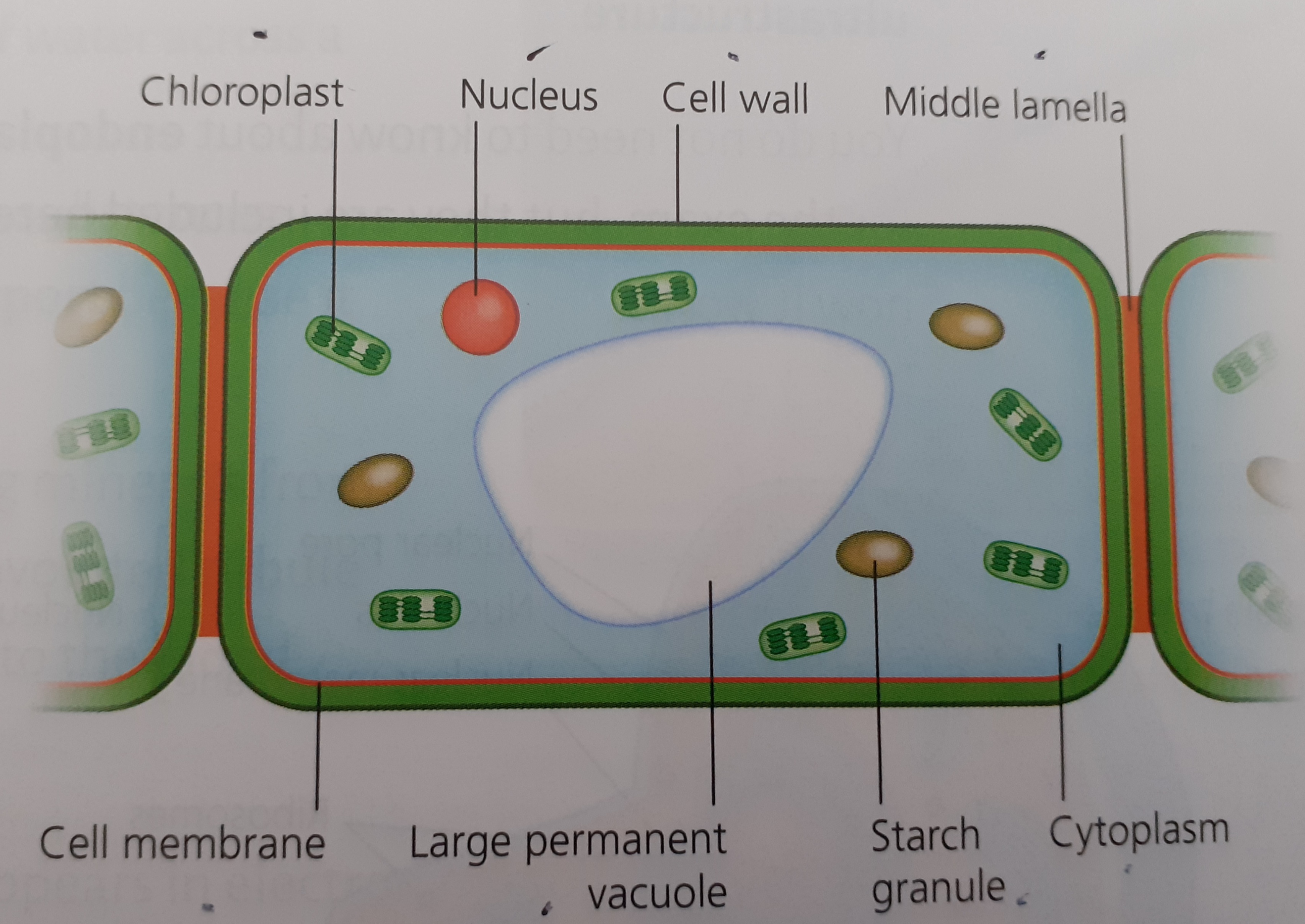
Plant Cell Ultra-Structure
Cells → Tissues → Organ → Organ system → Organism
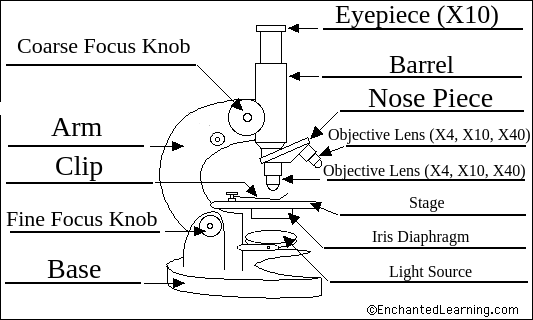
Microscopes
Cells are very small and can only be seen using a microscope
A microscope magnifies objects
A light microscope shines a beam of light through the specimen and magnifying lenses
An electron microscope uses a beam of electrons and obtains a much higher level of magnification

Organelles
Cells contain a variety of internal structures called organelles
An organelle is a cell component that performs functions for the cell
Cell Membrane
Cell Membranes are made up of phospholipids and proteins
The phospholipids and proteins are in constant motion
Membranes are said to be fluid
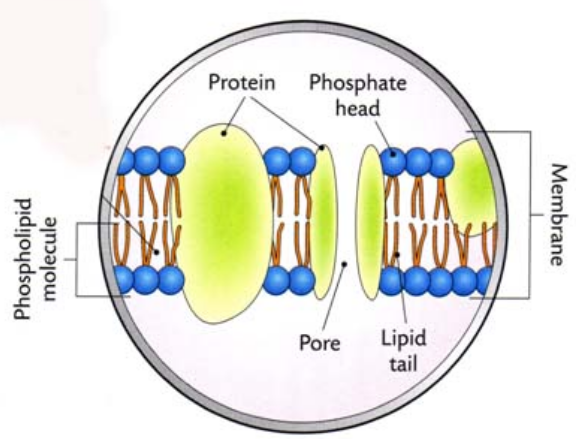
Functions of Cell Membranes
- Separate the cell organelles and cytoplasm from the outside
- Semi permeable - allows some molecules freely into and out and others to enter
- Membranes give some support to the cell
- Membranes recognise molecules that touch them
Nucleus (Often known, as the brain of the cell)
A large organelle near the center of the cell is the nucleus
The control center of the cell is the nucleus
It contains the cell’s genetic information
It controls the activities of the cell
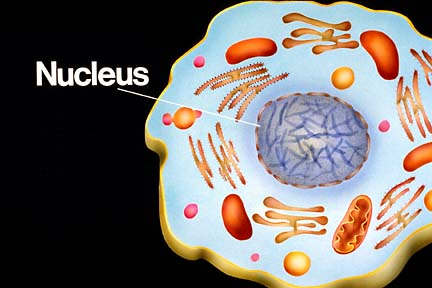
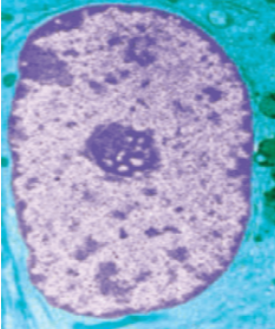
Ultra Structure of The Nucleus
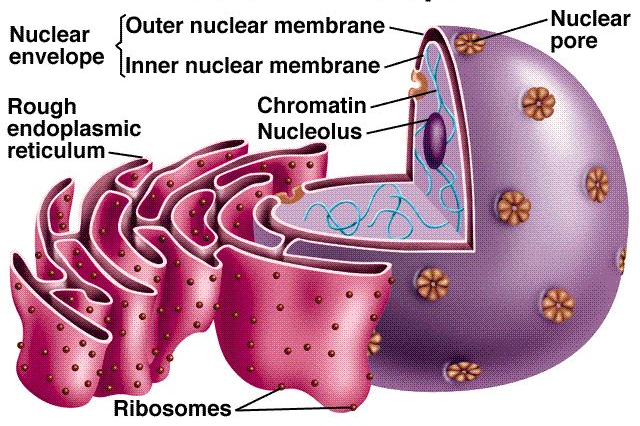
What’s in a nucleus?
The nucleus is made up of a double membrane with numerous nuclear pores
These control the movement of substances into and out of the nucleus
A nucleolus which contains RNA, DNA, and Proteins and it makes Ribosomes
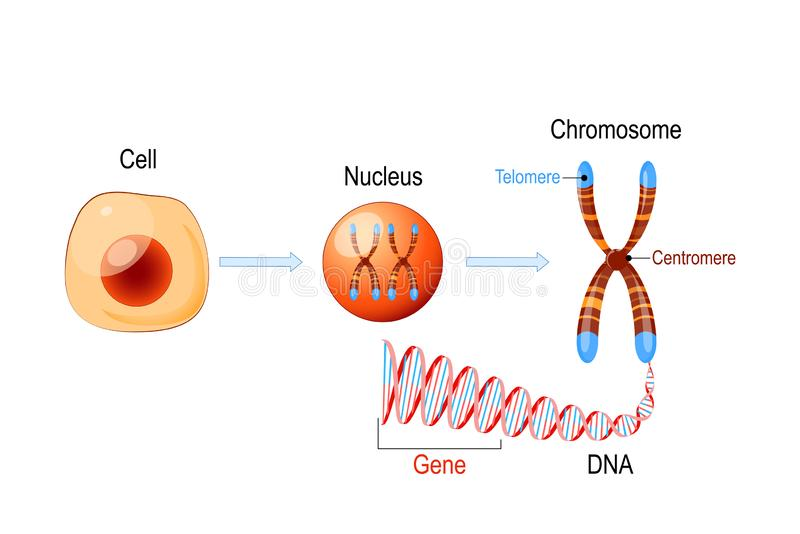
Chromatin which contains DNA that is arranged into chromosomes which stores our genes
Since DNA cannot leave the nucleus, genetic information is copied into molecules of mRNA and sent out into the cytoplasm. This information is used to manufacture Protein
It is enclosed by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope
Openings in the nuclear envelope called nuclear pores allow for movement of substances in and out of the nucleus
Structures inside the nucleus that contain DNA and proteins are called Ribosomes
DNA = Deoxyribonucleic acid
Mitochondria
Mitochondria supply energy to the cell in a process known as respiration
Cells with lots of mitochondria produce a lot of energy
The inner membranes of the mitochondria produce the energy
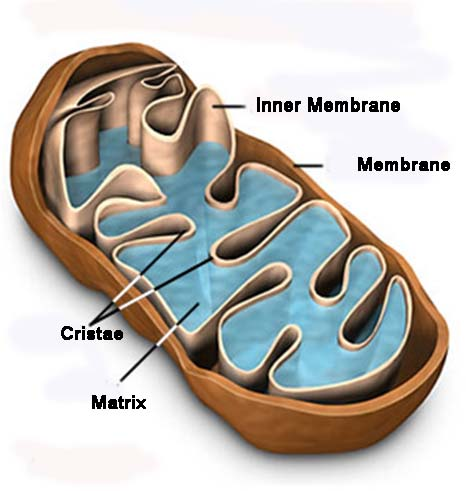
The more folds a mitochondrion has the more energy it produces
Ribosomes
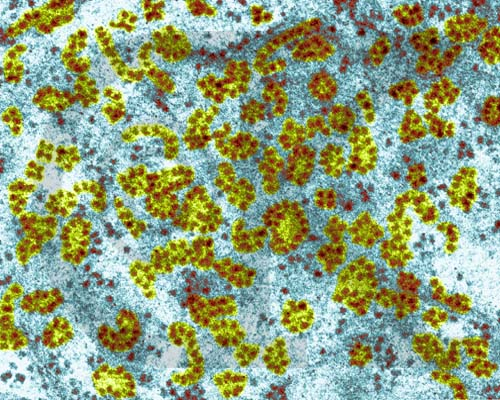
Ribosomes can be seen as red dots in this cell
Their function is to make proteins
Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm is a clear jelly like fluid that fills the cell
It contains all the organelles within the cell
When the cell cytoplasm fills with water, it pushes the cell membrane against the cell wall making the cell turgid (rigid and firm). When the plant is short of water, the cells become flaccid (soft) and the plant wilts
Chloroplast
The function of chloroplasts is Photosynthesis
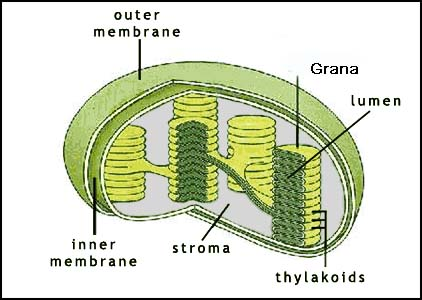
The thylakoids contain the chlorophyll which traps the sun’s energy
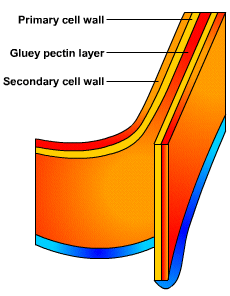
Cell Wall
The cell wall is rigid and gives plant cells a very defined shape.
The cell wall is composed of cellulose fibre, polysaccharides, and proteins.
The function of the cell wall is to support and strengthen the cell.
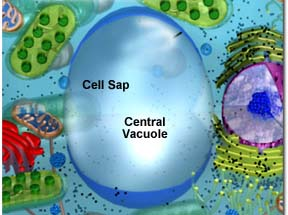
Vacuoles
Vacuoles are membrane-bound sacs within the cytoplasm of a cell
Vacuoles provide structural support, as well as serving functions such as storage, waste disposal, protection and growth.
Plant cells have large vacuoles
DNA
(no notes here yet)
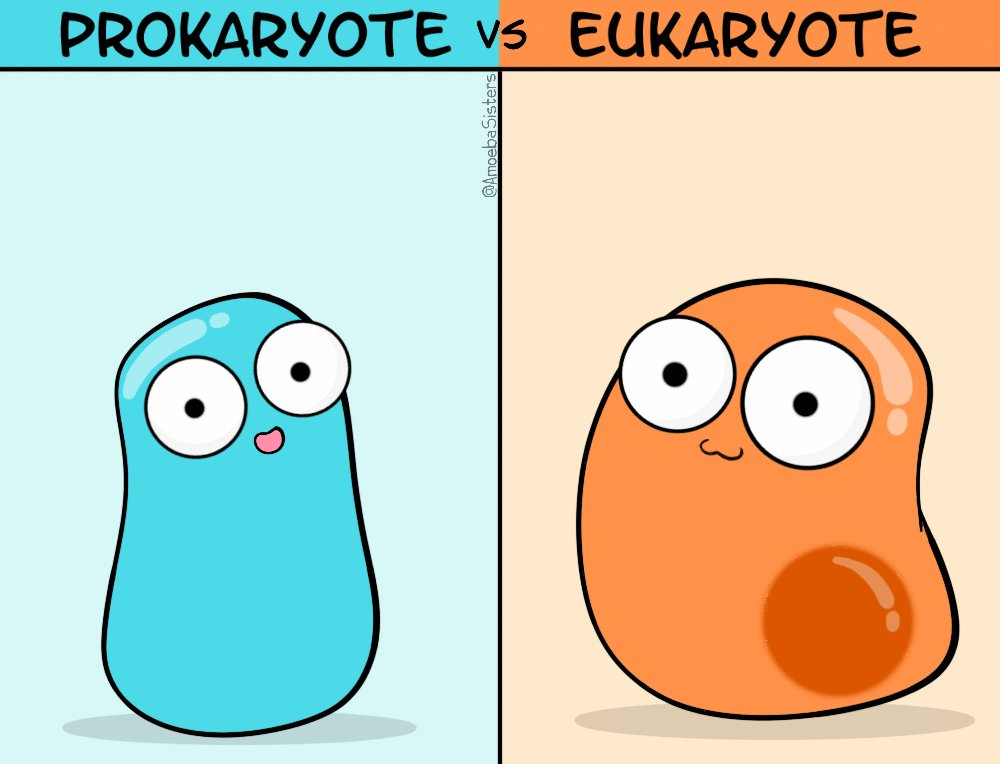
Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
Organisms whose cell contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles are called eukaryotes, e.g, plants & animal
Organisms whose cells never contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles are called prokaryotes, e.g bacteria
Tissue Culture
Tissue culture is the growth of cells in or on a sterile nutrient, artificial medium outside of the body
In vitro means outside the body
In vivo means inside the body
Examples
- Growth of skin: Skin is grown outside the body (often from stem cells) and new skin is grafted onto the wound
- Micropropagation: Growth of large numbers of plants from cells of a parent plant. It’s an inexpensive way to produce large numbers of similar plants
Tissues
A tissue is a group of similar cells that carry out a particular function
Plant Tissues
Dermal Tissue
A simple layer of strong cells (adaptation) **that surrounds the different parts of a plant
Epidermis: Protects the plant
Vascular Tissue
Transports materials around the plant via hollow tubes (adaptation)
Xylem transports water and minerals around the plant.
Phloem transports food from the leaves to the other parts of the plant
Animal Tissues
- Muscle tissue can contract (adaptation)
- Nervous tissue composed of nerve cells called neurons (adaptation)
Organ
A structure made up of tissues that work together to carry out a specific function
Examples:
- Plant Organ: Leaf
- Animal Organ: Heart
Organ System
A number of organs working together to carry out one or more functions
Example:
- Circularly System
- Digestive System