Respiration
Definition: Respiration is the release of energy from food
- The food involved in respiration is usually glucose
- Internal respiration is controlled by enzymes which allow energy to be released in small amounts
- The energy is trapped in molecules called ATP
Types of Respiration
- **Aerobic Respiration** – the release of energy from food in the presence of oxygen Example: Humans
- **Anaerobic Respiration** The release of energy from food without requiring the presence of oxygen Example: Yeast
Aerobic Respiration
- Most living things get energy from aerobic respiration and are called **AEROBES**
- The energy stored in bonds in glucose is released and used to make ATP
- When ATP breaks down it supplies energy for all the reactions in a cell such as movement of muscles, growth of new cells etc.
Equation for Aerobic Respiration
Chemical Reaction: C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy
Word Equation: Glucose + Oxygen -> Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy
- Aerobic respiration is relatively efficient, 40% of the energy in glucose is used to make ATP
- Any energy not used to produce ATP is lost as heat
Energy Carriers
There are two main groups of Energy Carriers
Group 1
- a) ADP **(Adenosine diphosphate)** = low energy molecule, found in cells of all organism
- b) ATP **(Adenosine triphosphate)** = high energy molecule, stores and transports energy
Remember ATP is a source of energy for most cell reactions
ATP stores energy and transfers it to where it is needed
Group 2
- a) NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) = low energy
- b) NADH- = high energy molecule
Reactions
ATP + water -> ADP + P + energy i.e. Respiration
- Phosphorylation is the addition of phosphate to a molecule (+P)
- Molecules with letter P are used in Photosynthesis
Aerobic Respiration
Aerobic Respiration occurs in 2 stages:
- Stage 1: Glycolysis
- Stage 2: Krebs Cycle
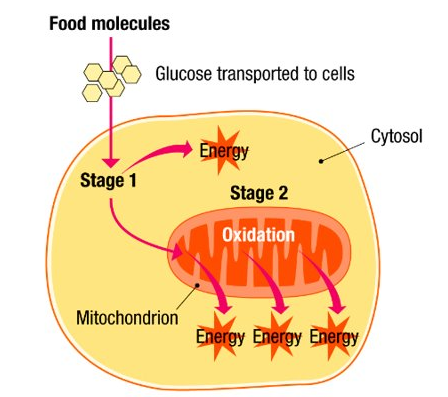
Cytosol = Cytoplasm without the organelles
Stage 1 - Glycolysis
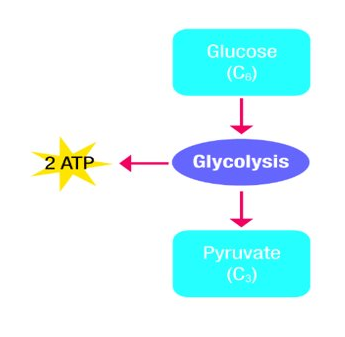
Glucose C6H12O6
Pyruvate = Pyruvic acid
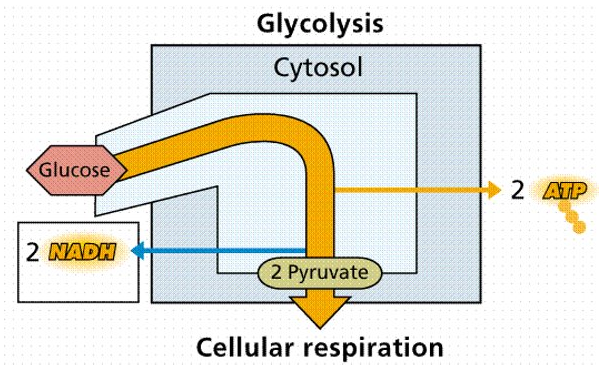
- Takes place in the cytosol (the cytoplasm without the organelles) as enzymes are found here
- Doesn’t require oxygen
- It only releases small amounts of energy
- Is the same for both aerobic and anaerobic respiration
- A 6 carbon carbohydrate (Glucose) is converted to two 3-carbon molecules with the release of a small amount of energy
- Most of the energy in the glucose molecule remains stored in each 3-carbon molecules
Stage 2 - Lumen and Mitochondrian
Stage 2 has two parts:
- Kreb Cycle
- Electron Transport System
1. Kreb Cycle
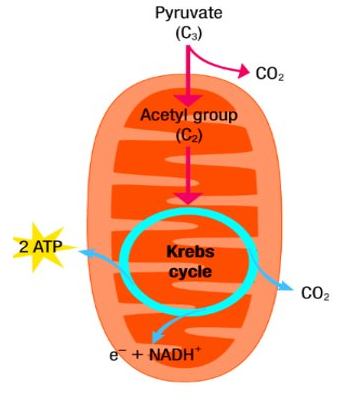
- Protons (H+) released (2H x4)
- Energy in Acetyl Co A released (electrons)
- ADP is conerted to ATP
NADH & CO2 (Main products formed)
- In the presence of oxygen the pyruvic acid enters the lumen in the mitochondrion KREBS CYCLE
- It loses a carbon dioxide molecule to form a 2-carbon molecule called Acetyl coenzyme A (Acetyl CoA for short)
- Pyruvic acid also loses 2 high energy electrons that combine with NAD+ and a proton to form NADH
- Each NADH will enter an electron transport system
- The Krebs cycle converts the acetyl group in CO2 and hydrogen
- The CO2 is released as a waste gas
- NADH+ is generated from NAD+ and the hydrogen
2. Electron Transport System
- The NADH enters and electron transport chain made up of protein molecules
- Takes place in the cristae of the mitochondria
- Oxygen is necessary
- The foldings of the cristae increase the number of electron transport systems that can fit in them
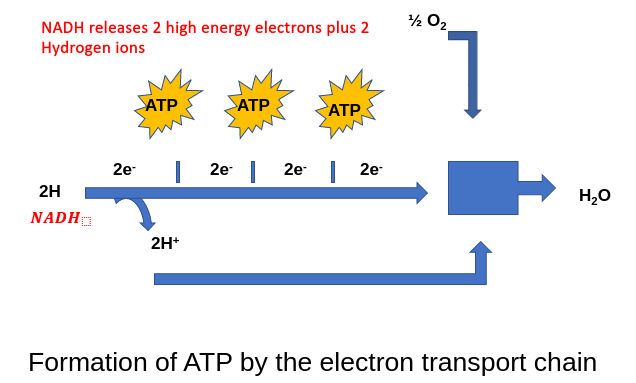
- High energy electrons are passed from NAD+H2 to the first of these molecules
- As electrons pass from molecule to molecule they lose some of their energy
- Some of this energy is used to form ATP the rest is lost as heat
- At the end of each system the low energy electron is removed by combining it with oxygen and hydrogen to form water
- The production of ATP by the electron transport system is called Oxidative Phophorylation as it requires oxygen + phosphate
- The main significance of the electron transport system is that it produces energy rich ATP
- Oxygen is essential as it accepts the low energy electron at the end of the chain
- If oxygen is absent aerobic organisms may die as there is no oxygen to accept the low energy electron and no ATP may be formed
Anaerobic Respiration
(also known as fermentation)
If oxygen is not present, the pyruvic acid (pyruvate) is converted into either lactic acid or ethanol and CO2
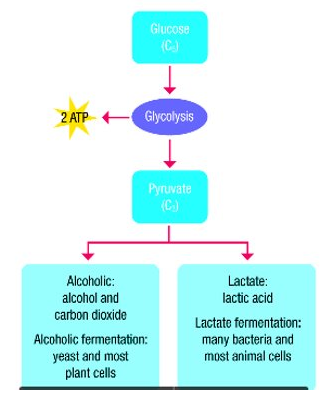
Lactate Fermentation Note: cheese, yoghurt production. 2. Lactic Acid - stitch after exercise
Alcoholic Fermentation Note: Sugar –yeast–> Alcohol + CO2
Anaerobic Respiration = Fermentation
As only stage 1 is involved in anaerobic respiration it only occurs in the cytosol
- Anaerobic respiration can occur in the presence of oxygen but it does not need to use it
- In anaerobic respiration Glycolysis occurs this means glucose is broken into two 3-carbon molecules
- A small amount of energy is released this way
Lactic Acid Fermentation
- This occurs in some anaerobic bacteria and fungi and in animal muscles when there is not enough oxygen
- In this fermentation Lactic acid is produced
- Glucose –> 2 Lactic Acid + small amount of energy pyruvate
- Biotechnology refers to the use of living things (such as microorganisms and enzymes) to carry our useful reactions
- In industrial fermentation the microorganisms are placed in a container with a suitable substrate on which they can react
- The vessel in which biological reactions can take place is called a Bioreactor

Advantages of Immobilised Cells
- Immobilisation is gentle it does not damage cells
- Immobilised cells can be easily recovered
- Immobilised cells reduce the need for filtration at the end of bioprocessing
- Immobilised cells can be reused reducing costs
Differences between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
| Aerobic | Anaerobic | |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Cytoplasm and Lumen and Cristae of mitochondria | Cytoplasm |
| Oxygen Requirements | Use O2 | Doesn’t use O2 |
| End Products | CO2 + H2O | Ethanol + CO2 or Lactic Acid |
| Energy Produced | Lots of energy (38 ATP) | Little energy (2 ATP) |
Syllabus Can You?….
- Definition of the term: aerobic respiration.
- Explain the role of aerobic respiration – what does it do for organisms?
- Express aerobic respiration by a balanced equation.
- State the nature of respiration from syllabus – what stages are involved, where do these take place, what happens?
- Definition of the term: anaerobic respiration.
- Express anaerobic respiration by a balanced equation.
- State the nature and role of fermentation.
- State the cellular location of the first & second stage.
- Explain the role of microorganisms in fermentation.
- Explain the role of microorganisms including bioprocessing and Bioreactors