Genetic inheritance
Definitions
- Heredity - The passing of features from one generation to the next
- Genetics - The study of heredity
- Fertilisation - The fusion of male and female gametes to form a diploid zygote
- Gametes - Haploid cells capable of fusion
Terms
| Terms | Definition |
|---|---|
| Monohybrid | One trait |
| Bihybrid | Two traits |
| Homozygous | Same form (two identical alleles) |
| Heterozygous | Different (two different alleles) |
Sex Chromosomes
- We have 46 chromosomes, or 23 pairs
- Autosomes are non sex chromosomes - We have 44 Autosomes (no. 1 - 22)
- The other 2 chromosomes are the sex chromosomes: the X chromosome and the Y chromosome
- Males have XY
- Female have XX
- All embryos start life as female
Alleles
- Alternative forms of genes
- Units that determine heritable traits
- HAIR COLOUR is the GENE
- BLOND, BLACK, RED are all ALLELES
- CHIN is the GENE
- SQUARE and ROUND are the ALLELES
Genetic Terms
- Alternative forms of genes
- Dominant alleles (TT - tall pea plants)
- Dominant (uppercase letter) - allele that is always expressed if present
- Recessive (lowercase letter) alleles (tt - dwarf pea plants)
- Recessive - the allele that is prevented from being expressed by dominant allele
Phenotype
- Outward appearance
- Physical characteristics
- Examples:
- Tall pea plant
- Dwarf pea plant
- Brown eyes
Genotype = Genetic make up of an organism
- TT (homozygous dominant)
- tt (homozygous recessive)
- Tt (heterozygous)
Non-nucleur DNA = DNA which is found in mitochondria and chloroplast which can also be inherited via the egg ovum
Most DNA is found in chromosomes in the nucleus
(Only the head of the sperm fuses with the egg so if we get DNA from mitochondria it comes from the egg)
Punnett Square
- A punnett square is used to show the possible combinations of gametes
- T = tall pea plant
- t = dwarf plant
- Phenotype of parent = Tall pea plant x Dwarf pea plant
- Genotype of parent = TT x tt
- Genotype of gamete =
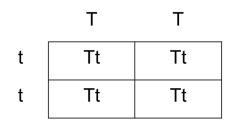
- Genotype of progeny (first generation of progeny) = Tt
- Phenotype of F. = Tall plants (all)
- Mendel’s first law of segregation: Genes separate during gamete formation
- Gametes fuse together
- F1 generation together
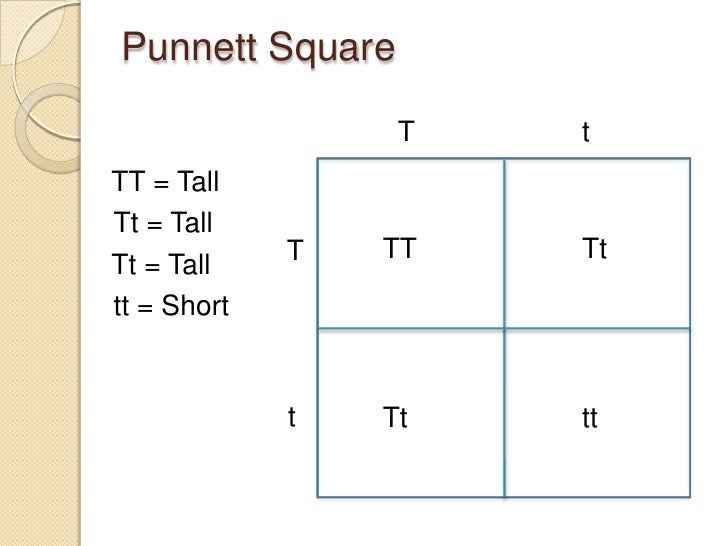
- Genotype of F2 progeny = TT Tt Tt tt
- Phenotype of F2 progeny = 3 Tall, 1 dwarf
Incomplete dominance (codominance)
_
Linked Genes = Genes that are located on the same chromosomes and are therefore inherited together

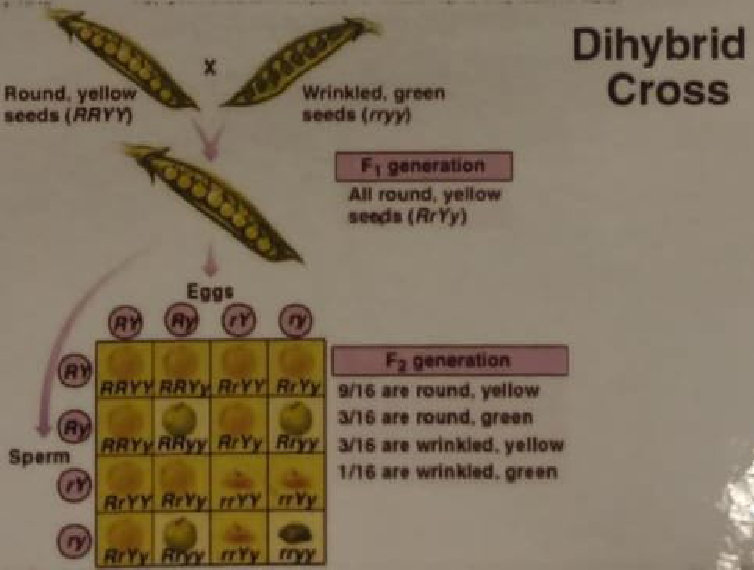
- DiHybrid Cross = cross involving two characteristics at a time
- Example: Dwarf White Pea Plant x Tall Red Pea Plant
- T = tall
- t = dwarf
- R = red
- r = white
- Genotype of Dwarf White Pea Plant = ttrr
- Genotype of Tall Red Pea Plant = TtRr or TTRR or TTRr or TtRR
Mendel’s 1st Law of Segregation
Only one member of a pair of alleles enters a gamete
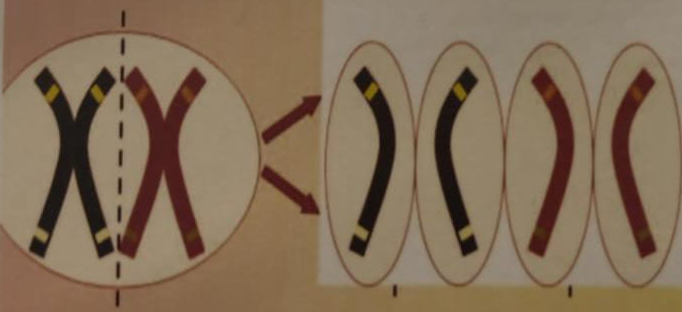
Mendel’s 2nd Law of Independent Assortment
Either member of a pair of alleles has an equal chance of entering a gamete with either member of any other pair of factors
DiHybrid Cross Example with Pea Plants
- Parent Phenotype: Dwarf White x Tall Red
- Parent Genotype: ttrr x Tr Rr
- Gametes: tr x TR Tr tR tr
Cross:
| TR | Tr | tR | tr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| tr (This is crossing with the gametes on top) | TtRr | Ttrr | ttRr | ttrr |
- Genotype of F1: TtRr, Ttrr, ttRr, ttrr
- Phenotype of F1: Tall Red, Tall White, Short Red, Short White
- Ratio: 1 (25%) : 1 (25%) : 1 (25%) : 1 (25%)
DiHybrid Cross Example with Guinea Pigs
- B = black coat
- b = white coat
- S = short hair
-
s = long hair
- Phenotypes = Black coat and short hair, White coat and long hair
- Genotypes = BbSs, bbss
- Table:
| bs | |
|---|---|
| BS | BbSs |
| Bs | Bbss |
| bS | bbSs |
| bs | bbss |
- Genotypes of F1 Progeny = BbSs, Bbss, bbSs, bbss
- Phenotypes of F1 Progeny = Black coat and short hair, Black coat and long hair, white coat and short hair, white coat and long hair
- Ratio = 1 : 1 : 1 : 1
Linked Gene Example
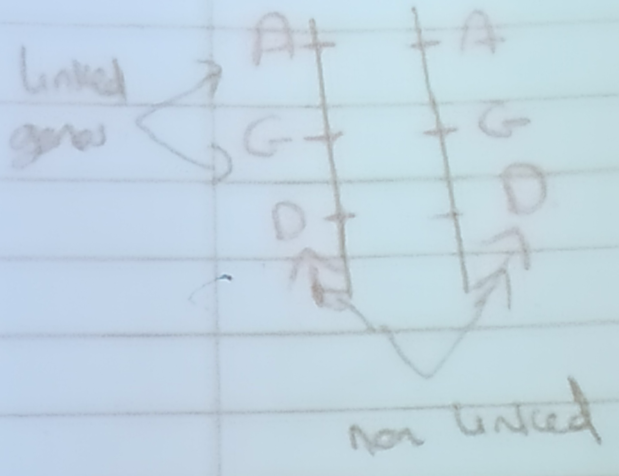
- Linked Genes = Genes that are located on the same chromosome + inherited together
- Genes that are linked don’t obey the law of independent assortment (2nd law - Mendels)
- Fruit flies = Drosophilia Melanogarter
- Often used in genetic crosses
Example using Fruit Flies 1
- Long Wings (L) OR Vestigial (Short) Wings (l)
- Wide abdomen (W) (Homozygous Dominant) OR Narrow abdomen (w) (Homozygous Recessive)
- Parent Phenotype: Long Wing, Wide Abdomen x Vestigial Wing, Narrow Abdomen
- Parent Genotype: LW, LW x lw, lw
- Gametes: LW x lw
- Cross:
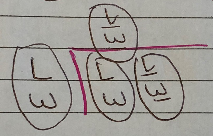
(No need to do cross when outcome is obvious)
F1 Phenotype: LW, lw
Example using Fruit Flies 2
- Parent Phenotype: Long wing wide abdomen (Heterozygous) x Long wing wide abdomen (Heterozygous)
- Parent Genotype: LW, lw x LW, lw
- Cross:
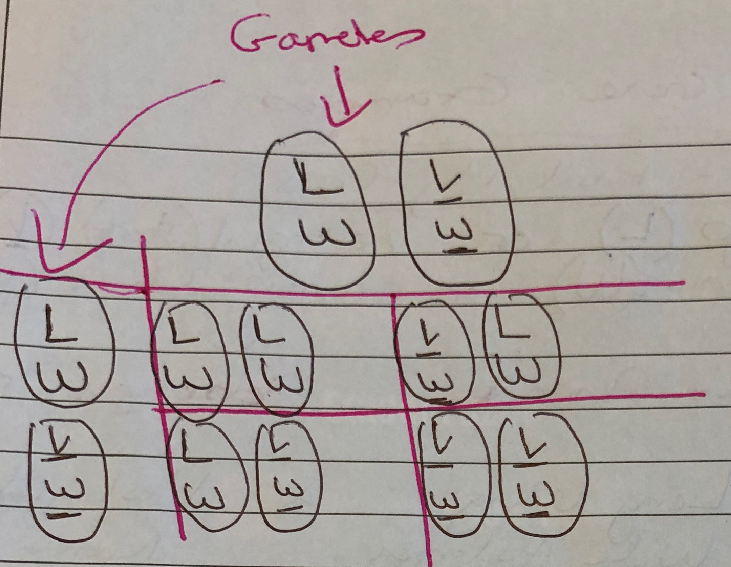
- F1 Genotype: LW, LW x lw, LW x LW, lw x lw, lw
- F1 Phenotype: Long & Wide x Long & Wide x Long & Wide x Vestigial (Short) & Narrow
Sex Linkage
- Sex Linked Genes - Genes found normally on the X chromosome (recessive gene)
- Carrier - A female who has an allele for the abnormal condition but doesn’t how it
Hemophilia
- Normal Blood = N
- Hemophilia = n
- Female = XX
- Male = XY
- Normal (Carrier) = Female: XNXn Male: –
- Normal (Non Carrier) = Female: XNXN Male: NY-
- Hemophilia = Female: XnXn Male: XnY-
Example
- Red-green colour blindness is a sex-linked trait. If a normal man has a child with a carrier woman. What is the likelihood that their first son would be colourblind?
- Non-colourblindness = C
- Colourblindness = c
- Parent Phenotypes: Normal Male x Carrier (for colourblindness) Female
- Parent Genotype: XCY- x XCcn
- Cross:
| XC | Y- | |
|---|---|---|
| XC (Being Crossed with Above) | XCXC | XCY- |
| Xc (Being Crossed with Above) | XCXc | XcY- |
- F1 Genotype: XCXC, XCY-, XCXc, XcY-
- F1 Phenotype: Normal Female, Normal Male, Carrier Female, Colourblind Male
- Answer: 25% Chance of Colourblindness in Children
Heredity
- Heredity is the passing on of features from parents to offspring by means of genes
- Also called Genetic Inheritance
Genes
- A gene is a length of DNA that codes for a specific protein
- It is the unit of inheritance
- It is found on a chromosome
- It contains instructions to make a particular protein
- Characteristics are controlled by genes
Gene Expression
- Not all genes are expressed
- E.g. Gene for Tallness
- Organism is small - Why?
- Maybe due to poor nutrition
- Characteristics (phenotype) = heredity + environment
Heredity is the passing on of features from parents to offspring by means of genes. A gene is the unit of inheritance. They are found on a chromosome. They contain instructions to make a particular protein. Gene expression is the way in which the blueprint in a gene is decoded.
Chromosome
- _
- Chromosomes are made up of (60%) protein and (40%) DNA
- Genes are arranged along the DNA of the chromosome
Non Coding DNA
- Large sections of the chromosomes don't contain genes
- This DNA is called Non Coding DNA
- It’s function is not yet clear
- Sometimes called “Junk DNA”