Cell Division
Syllabus - Objectives (OL)
- Explain the terms: cell continuity & chromosomes
- Define the terms: haploid & diploid number
- Describe the cell activities in he state of non-division: Interphase and Division (mitosis)
- Define the term: mitosis
- Explain the process in simple terms with some diagrams
- Define cancer and state causes
- State the primary function of mitosis for single-celled vs multi-cell. Organisms
- Define the term: meiosis
- State the functions of meiosis
Cell Continuity
Definition: Cell continuity (= cell division) means that all cells develop from pre-existing cells
3 steps to form a new cell
- Produce materials it will need
- Grow larger
- Reproduce to form a new cell
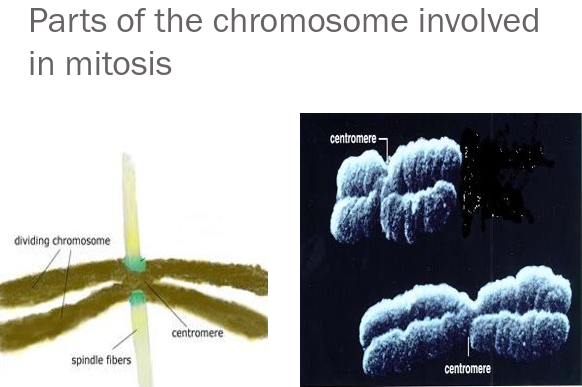
Chromosomes
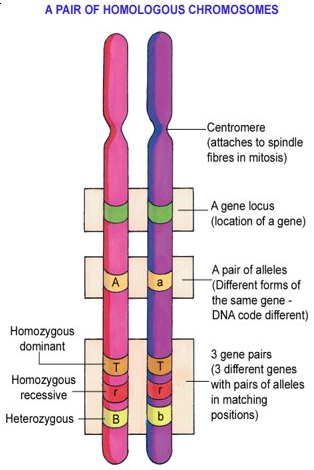
- Definition: Chromosomes are structures in the Nucleus, made of DNA & Protein
- Not dividing = Chromatin (long thing threads)
- When dividing = Chromatin forms a numbers of clearly distinguishable Chromosomes
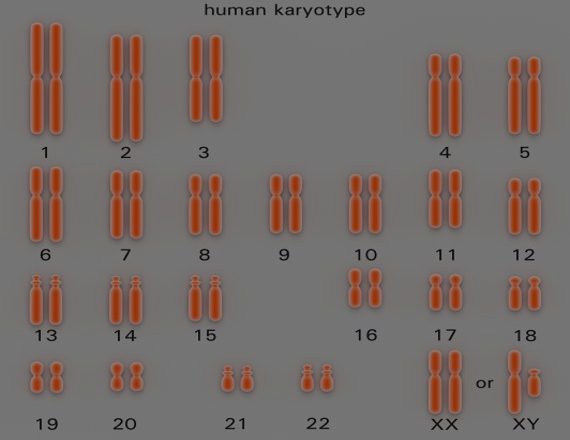
- Each species has a definite no. of Chromosomes, Humans = 46 chromosomes
- Each Chromosome has 1000s of genes (Check out human genome project). Each cell in the human body contains about 25,000 to 35,000 genes
Haploid
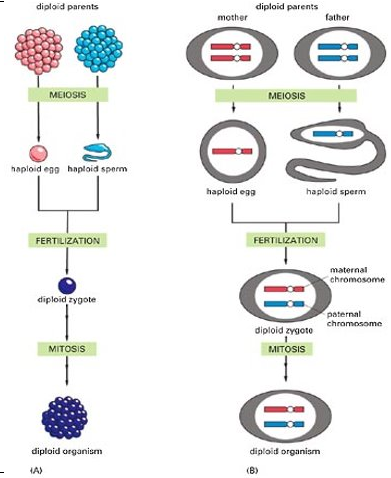
Definition: A Haploid cell has one set of each type of chromosomes, ie. has only one set of each type of chromosomes in the nucleus
Haploid is symbolised by letter 'n' and number of chromosomes in the cell is given as n=23
In humans, eggs and sperm are haploid n=23
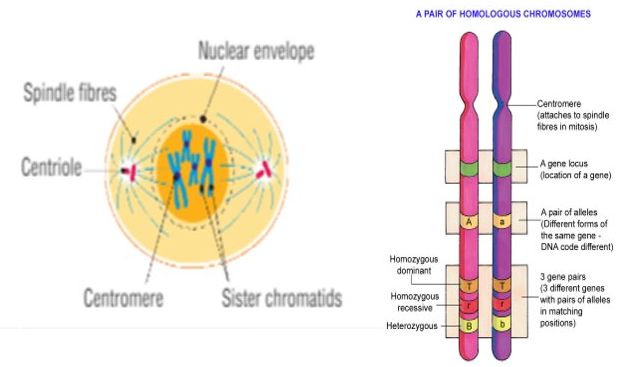
Diploid
Definition: A diploid cell has two sets of each type of chromosomes, ie. It has two of each type of chromosome in the nucleus
Chromosomes are in pairs in diploid cell, called homologous pairs. (Both chromosomes same size and shape)
(Homologous = same length, similar)
Diploid is symbolised as ‘2n’ and total no. of chromosomes in cell is given as 2n=46. This means there are 23 pairs of chromosomes
Triploid
Definition: A triploid cell has three sets of chromosomes
Somatic Cells
- Somatic cells are normal body cells of an advanced organism and contain two sets of chromosomes (not sex cells)
Somatic Cells -> Diploid Sex Cells -> Haploid
- In diploid cells, 1 chromosome from the homologous pair comes from the mother and the other comes from the father
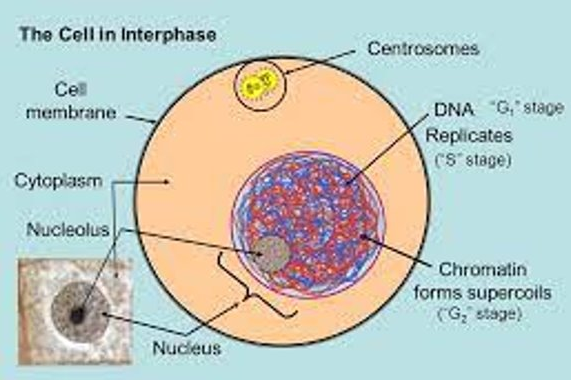
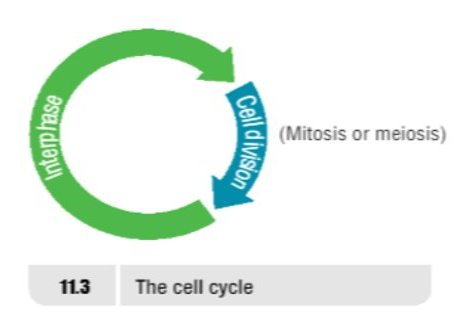
Cell Cycle
- Describes the life of a cell. It includes the period between division when the cell is not dividing, called Interphase
- Period when a cell divides = Mitosis
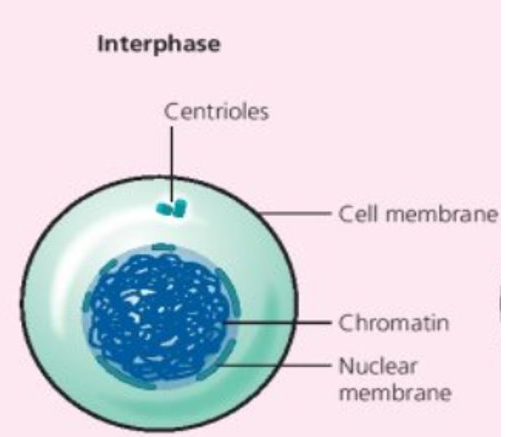
Interphase
- Longest phase in cell cycle = 90% of a cells life is in interphase
- Chromosomes elongated = chromatin
- Cell very active in Interphase, produces new mitochondria, chloroplasts etc. and chemicals needed for growth
Mitosis
Definition: Mitosis is a form of nucleur division in which one nucleus divides to form two nuclei, each containing identical sets of chromosomes
Two new cells called daughter cells and they are IDENTICAL to each other
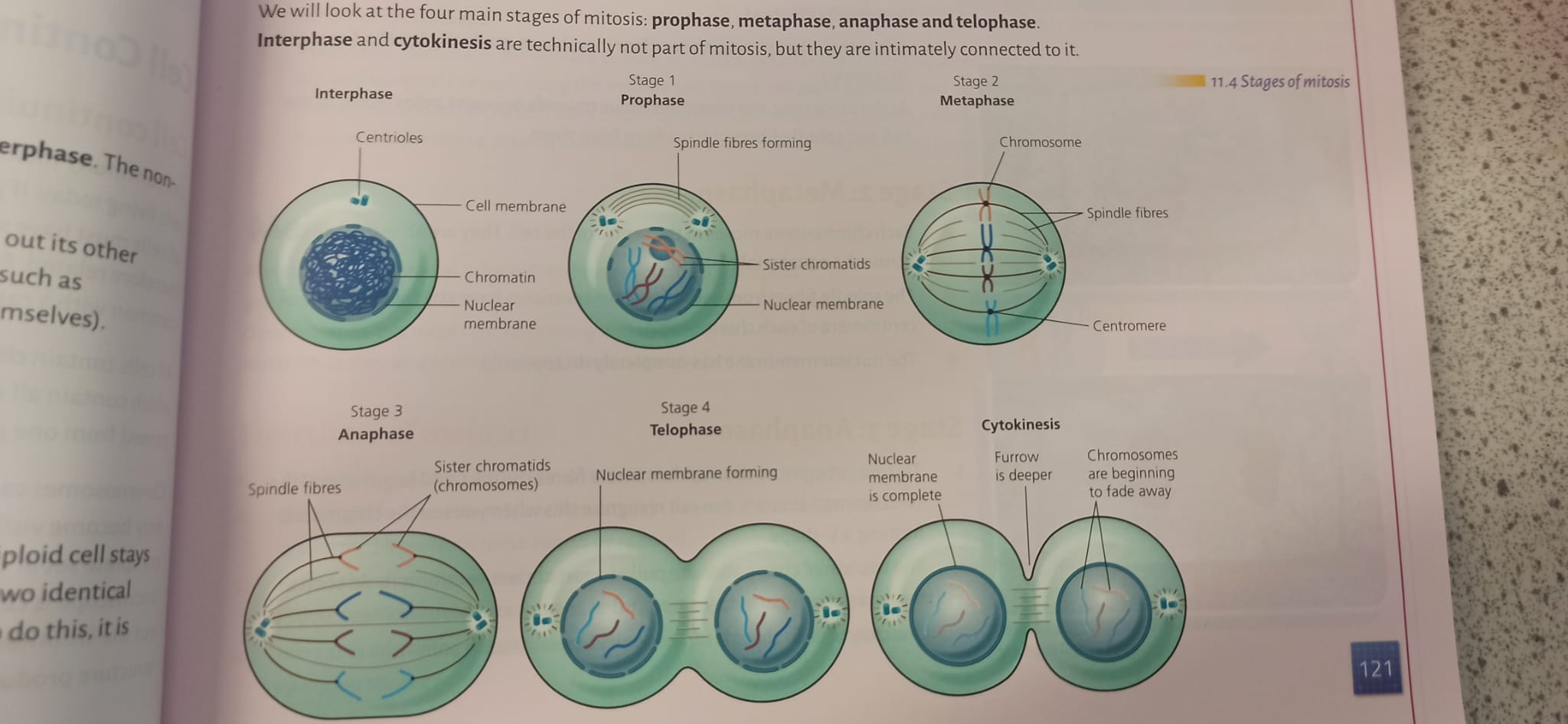
Stages of Mitosis (4 in total)
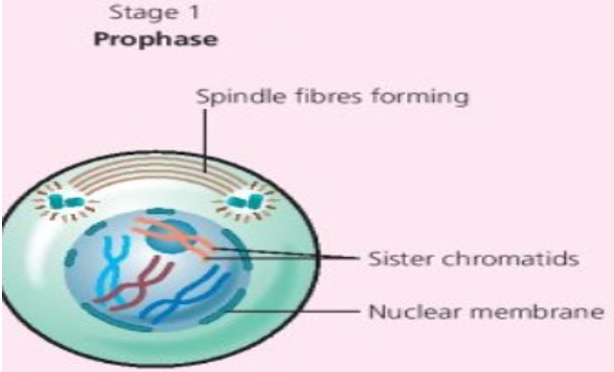
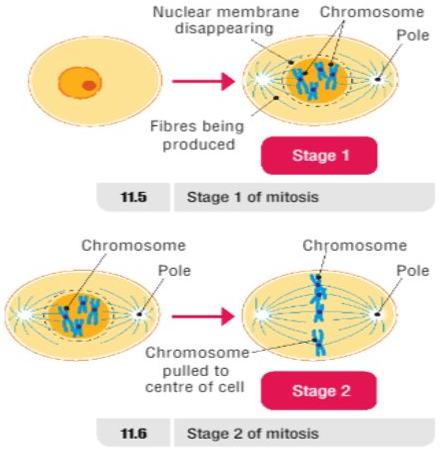
Stage 1 Prophase (HL)
- At end of Interphase, Chromosomes contract and become visible
- Each chromosome appears as a duplicated strand
- Fibres appear in cytoplasm
- Nuclear membrane starts to break down
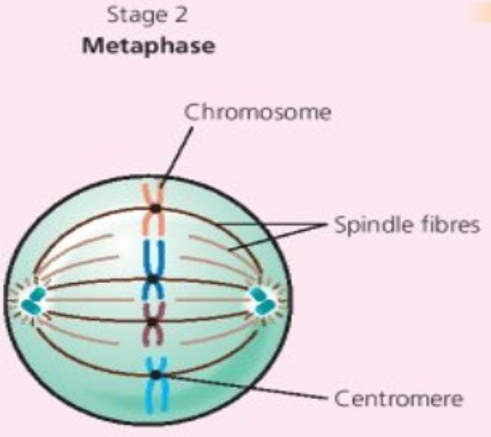
Stage 2 Metaphase (HL)
- Nuclear membrane broken down
- Chromosomes thicken even more
- Chromosomes line up across the centre of cell along equatorial plate
- Fibres produced by centrioles attach to chromosomes
- Each chromosome has 2 fibres attached, 1 from each side of the cell
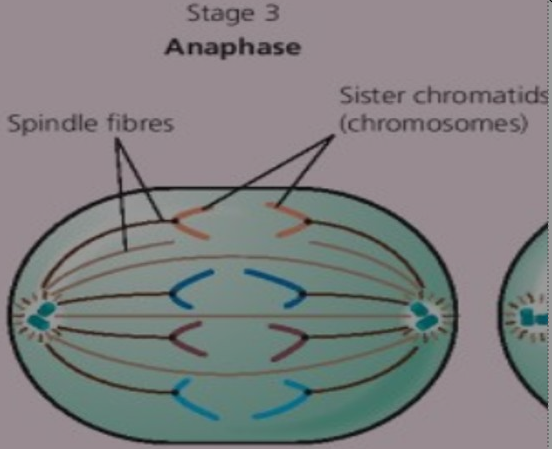
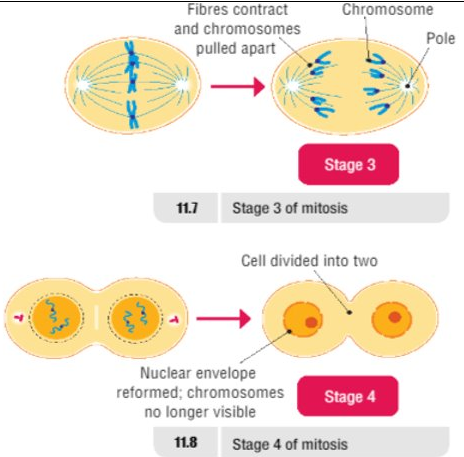
Stage 3 Anaphase (HL)
- Fibres contract, chromosomes pulled apart
- Each strand of chromosome is pulled to opposite end of cell
- Hence, identical set of genes pulled to each end of the cell
- (Look for V shape to recognize this stage)
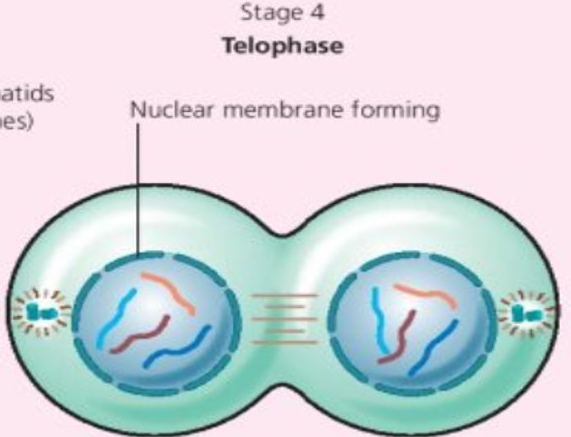
Stage 4 Telophase (HL)
- Nuclear membrane forms around each of the 2 sets of chromosomes
- Chromosomes elongate within each nucleus
Mitosis is complete
Once complete, original cell divides to form 2 cells. In reality there are 5 stages - see Pg 123 (of textbook) Cytokinesis
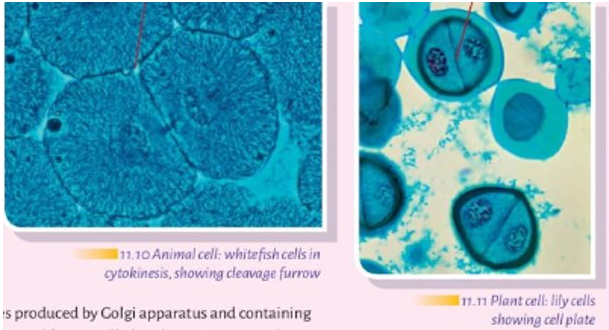
Functions of Mitosis
In Unicellilar Organisms
- Method of reproduction for Amoeba Reproduction that doesn’t involve the joining of 2 cells is called Asexual reproduction
In Multicellular Organisms
- Produces new cells, not new individuals
- Responsible for growth & renewal and repair of cells (growth + repair cells)
Cancer
- Rate of cell division (mitosis) is carefully controlled
- Sometimes a cell or group of cells lose the ability to control the rate of cell division
- They form a mass of cells called a tumour which can be benign or malignant
Benign tumours
- Benign means kind, they are not life threatening and do not invade other tissues. E.g. warts, skin tags
- Cells stop dividing after some time
Definition: Cancer occurs when certain cells lose their ability to control the rate of mitosis
Malignant tumours
- Uncontrolled multiplication of abnormal cells
- Malignant tumours (cancers) invade other cells and move around the body
- Movement of these cells called Metastasis
- Cancer cells divide indefinitely
Causes of Cancer
- Caused when normal genes are altered to form cancer causing genes called oncogenes
- Brought about by cancer causing agents called carcinogens e.g. cigarette smoke, asbestos fibres,, ultraviolet radiation and some viruses
- Most cancers can be cured with Radiation (burn out cancer), Chemotherapy (Chemicals slow down mitosis) and surgery
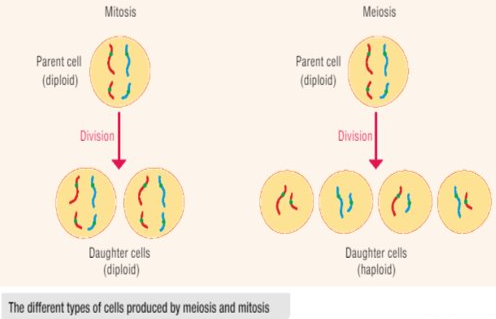
Meiosis (2nd Type of Cell Division)
- Definition: Meiosis is a form of nucleur division in which the daughter nuclei contain half the chromosome number of the parent nucleus
- Humans cells (somatic cells) have 46 chromosomes
- Meiosis occurs in the ovaries and testes to produce gametes called eggs and sperm so there are 23 chromosomes in each egg and sperm
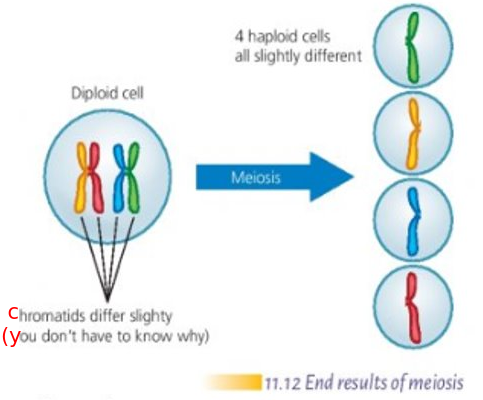
Functions of Meiosis
2 functions in Multicellular Organisms
- Allows sexual reproduction without increasing the number of chromosomes in the offspring
- Allows new combinations of genes
Differences between mitosis and meiosis
| Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|
| Produces two daughter cells | Produces four cells |
| The daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes as the parent | The daughter cells have half the number of chromosomes as the parent |
| The daughter cells are genetically identical | The daughter cells are genetically different |
Higher Level
A sentence to help you remember the 4 stages of mitosis (HL)
- I Party Monday And Tuesday
| Letter (Word) | What Letter Stands for |
|---|---|
| I | Interphase |
| P(arty) | Prophase |
| M(onday) | Metaphase |
| A(nd) | Anaphase |
| T(uesday) | Telophase |