Scientific Method
Areas of Study (You should know 3)
| Terms | Definition |
|---|---|
| Botany | The study of Plants |
| Genetics | The study of Genes and DNA |
| Physiology | The study of the Human Body |
| Biochemistry | The study of Chemicals in the Body |
| Ecology | The study of Nature |
| Microbiology | The study of Micro-Organisms |
| Horticulture | The study of Growing Plants |
Scientific Investigations
- Curiosity and observations lead to an idea/explanation of how something works
- Investigations into whether the idea is correct or not happen
- Sometimes the idea is correct and sometimes the idea is wrong
- The idea is shared with others, so they can investigate also
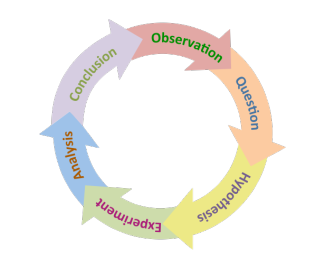
Scientific Method based on
- Making Observations
- Forming a Hypothesis (suggested explanation-educated guess (Hypothesis (prediction) can be tested))
- Design experiment
- Collect & Interpret Data
- Forming a conclusion
- Communication (Publication in SCIENTIFIC Journals (on the internet is not accepted answer in LC exam))
Definitions to Learn
| Terms | Definition |
|---|---|
| Hypothesis | An educated guess based on observations (“If … Then …”) |
| Experiment | A test for a hypothesis |
| Data | The information gathered in experiments |
| A Theory | An explanation based on repeated hypothesis and experimentation (Example: Theory of Evolution) |
| A Principle or Law | A principle or law arises from a theory when it is seen always to be true under all conditions over a long period of time (Example: Law of Gravity) |
Small Pox and the Scientific Method
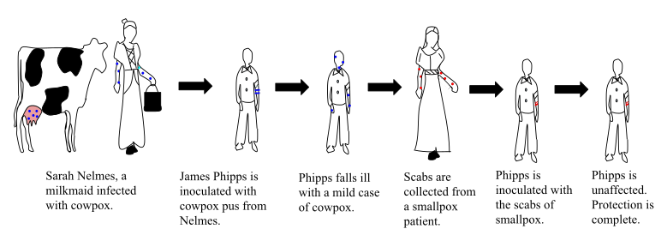
Example: Vaccinations
Observation
Milk maids do not get small pox (serious condition)
Hypothesis
Milk maids get cow pox (mild condition) which protects them from small pox
Experiment
Small boy was infected with cow pox and suffered cow pox. Two months later he was injected with small pox
Result
Boy did not suffer small pox
Conclusion
Cow pox protects from small pox. Cow pox fluid can be used to give immunity to small pox
Edward Jenner – Experiment 1796
Scientific investigations lead to…
When a hypothesis is confirmed it can lead to a Theory
E.g. Theory of Evolution
When a theory is confirmed over many years it becomes a Scientific Principle
When a Principle is judged to be of great basic importance it is called a Law
E.g. Law of Gravity
Hypothesis → Theory → Principle → Law
Limitations of the Scientific Method
Experiments are only based on current knowledge
Results are limited by our ability to interpret them
The natural world is in constant change (myxomatosis- rabbits now resistant to it)
Dishonesty
In 1998, a report claiming MMR vaccine had links to autism
Video: Not all scientific studies are created equal - David H. Schwartz
Accidents
The discovery of viagra
Sample Size
If the Sample Size is too small, results cannot be trusted
Experimental Design – A Fair Test
- Large sample size (if possible)
- Only one variable changes (fair test)
- Other variables remain constant
- Replicate: Repeat many times to verify result
- Use a control (a setup for comparison)
- Data must stand up to independent scrutiny
Terminology
| Name | Definition | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Qualitative Data | Descriptive/observations/subjective (Influenced by personal feelings) | Names, hair (color), nationality |
| Quantitative Data | Measurements/numbers/objective | Age, height |
| Independent Variable | The variable that is being changed | |
| Dependent Variable | The variable that changes as a result of the independent variable |
Drug Testing on Humans (Definition to Learn)
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| Placebo | An identical tablet to the one being tested but which does not contain the drug. This is the control group. |
| Blind Test | The individual does not know if they have received the drug or the placebo |
| Double Blind Test | The individual being tested and the test administrator does not know who is receiving the placebo |
Ethics
Throughout this course we will come across scientific issues which have ethical implications
Ethical issues relate to what is right and what is wrong