Nutrition (& Food)
Required for: Energy & Growth
Metabolism
All the chemical reactions that take place within a living organism
Can be subdivided into:
- Anabolic Reaction = building up simple molecules into more complex molecules
Example: Photosynthesis
Simple → Complex
- Catabolic Reaction = breaking down complex molecules into simpler ones
Example: Respiration & Digestion
Complex → Simple
Food is required for
- Energy - Food is broken down in cellular respiration to produce energy
- Provide building blocks for growth and repair of cells
- Metabolism - to produce the chemicals that take part in and control all the chemical reactions occurring in the body
Bio-Elements
6 Macro-nutrients (Main Elements): CHONPS
- Carbon (C)
- Hydrogen (H)
- Oxygen (O)
- Nitrogen (N)
- Phosphorous (P)
- Sulfur (S)
5 Micro-nutrients (Mineral Elements):
- Sodium (Na)
- Magnesium (Mg)
- Chlorine (CI)
- Potassium (K)
- Calcium (Ca)
3 Trace Elements:
- Iron (Fe)
- Copper (Cu)
- Zinc (Zn)
Bio-Molecules
Bio-Molecules - Chemicals that are made inside a living being
4 majors types found in food are:
- Carbohydrates
- Lipids
- Proteins
- Vitamins
Carbohydrates
Elements: C, H, O
Smallest Unit: Monosaccharide’s
Types:
- Starch - Stored in plants (Storage Role)
- Glycogen - Carbohydrate stored by animals (Storage Role)
- Cellulose - Found in cell walls of plants (Structural Role)
Metabolic Role - Broken down in respiration, provides energy
Food Sources:
- Breads
- Potatoes
- Rice
- Sugars
- Cakes
- Etc.
The general formula for a carbohydrate is
\[C_x(H_2O)_y\]There are twice as many hydrogen molecules as oxygen molecules
Most carbohydrates contain 6 carbons
A common carbohydrate
General formula = $C_x(H_2O)_y$
When x = y = 6 (6 is the most common value for x and y)
We got the formula $C_6H_{12}O_6$
The name of this monosaccharide carbohydrate: Glucose
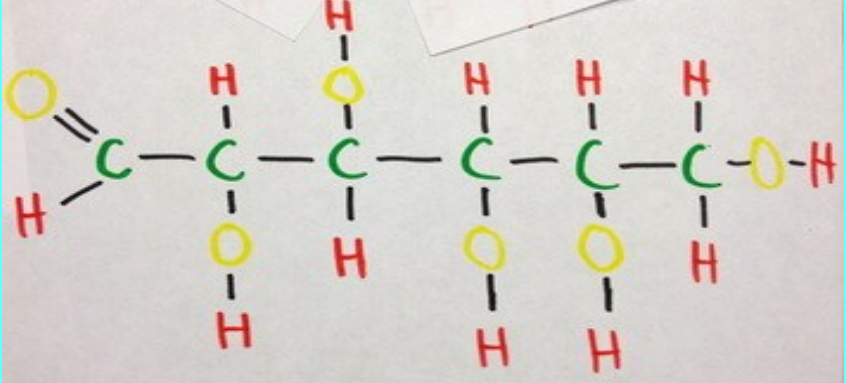
Another common carbohydrate
General formula = $C_x(H_2O)_y$
When x = 12 and y = 11
We get the formula $C_{12}H_{22}O_{11}$
The name of this disaccharide carbohydrate: Sucrose
Lipids(Fats/Oils)
Fat/Oils are types of lipids
Elements: C, H, O
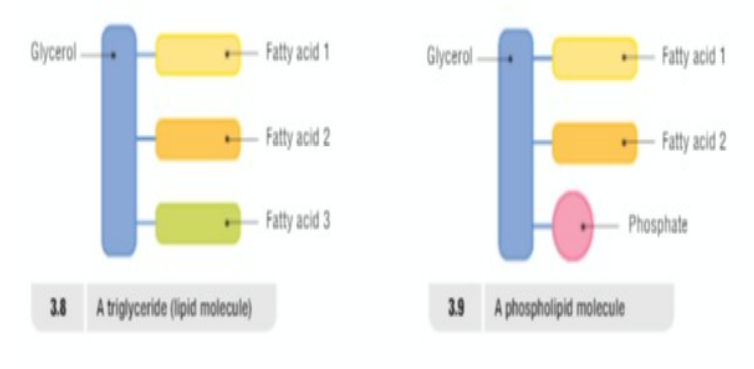
Smallest Unit: Triglyceride (One molecule of glycerol linked to three fatty acids)
Phospholipids: are fat like substances where one of the fatty acids is replaced by a phosphate group added to it
Types:
- Animal Fats
- Plant Oils
Metabolic Role: Broken down in respiration to provide energy
Structural Role: Store energy/insulate
Dietary Source: butter, oils, margarine, cream, etc.
Proteins
Elements: C, H, O, N
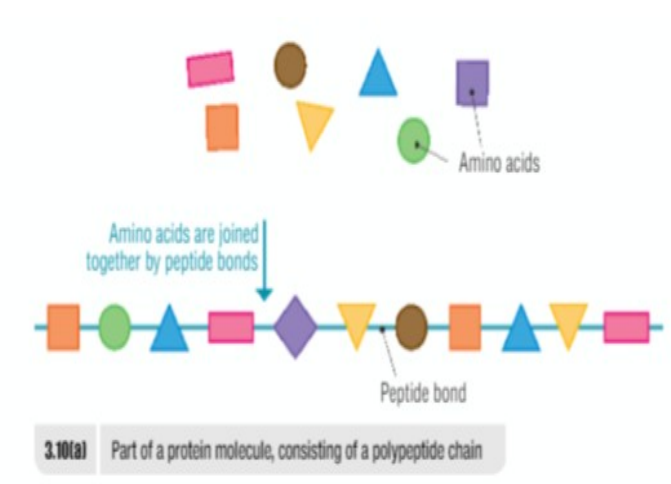
Proteins are composed of 20 common amino acids
Bond between amino acids is called a peptide bond
Smallest Unit: peptide
Peptide (<20 amino acids) - polypeptide(>20 amino acids) - protein(at least 200 amino acids)
Peptide → polypeptide → protein
Metabolic Role (folder proteins) - Used as enzymes to control reactions
Structural Role (fibrous proteins) - Found in e.g. keratin in hair, nails and feathers
Dietary Source: Meat, fish, egg, nuts, beans
Enzymes are substances that speed up or slow down reactions Example: Amylase (It is in saliva)
(Anabolic: small → big Catabolic (digestion): big → small)
Vitamins
- Organic compounds
- Cannot be made in the body
- Must be taken in the diet
- Required in very small amounts
- Essential for correct functioning of the body
- Often act as co-enzymes
- Lack of a vitamin causes a deficiency disease
- Named by letters
Water Soluble/Fat Soluble Vitamins
-
Water Soluble
-
Fat Soluble
- Vitamin C
-
Source: Citrus Fruits
- Vitamin D
-
Source: Dairy Products and Sunshine
- Functions:
- Forms connective tissue such as skin and gums
- Helps immune system
- Functions:
- Helps to absorb calcium needed for healthy bones and teeth
-
Deficiency: Scurvy = Poor healing of skin, gums. causing loss of teeth
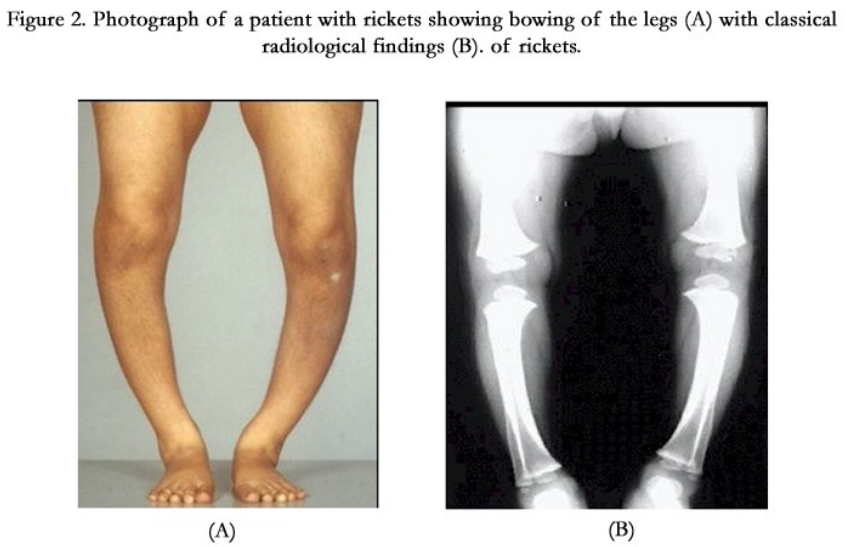
- Deficiency: Rickets = weak deformed bones
Minerals
- Inorganic nutrients in the form of dissolved salts.
- Humans:
- Iron for haemoglobin
- Calcium for healthy bones
- Plants:
- Magnesium for producing chlorophyll
- Calcium for cementing cell walls together
Water
- $H_2O$ – most abundant liquid on earth, vital for all living things
- Properties:
- Liquid at normal environmental temperatures
- Transport medium
- Solvent – lots of things dissolve in water
- High heat capacity – slow to warm up or cool down
- Surface tension
Importance of Water
5 reasons why water is so important
| Number | Term | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chemical Reactions | Involved in many chemical reactions e.g photosynthesis |
| 2 | Cell | Hydrates cell + keeps it firm (tugrid) |
| 3 | Transport | Al lipids in the body contain water (blood, urine, sweat) |
| 4 | Solvent | Excellent at dissolving substances |
| 5 | Temperature Control | Sweating cools the body |
There are 2 groups of autotrophs
Nutrition (and Ecology) Terms
| Term | Definitions | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Autotrophs (Producers) | An organism that makes their own food | Plants |
| Photosynthetic | Plants using light (photosynthesis) to make their own food | |
| Chemosynthetic | Organisms converting Nitrogen to Nitrates (plants use these to make protein) |