(A Search for a) Definition of Life & Characteristics of Life
All organisms have many features or characteristics in common
The Variety of Life
All living things are divided into two main groups
-
Plants

-
Animals

The Animal Kingdom
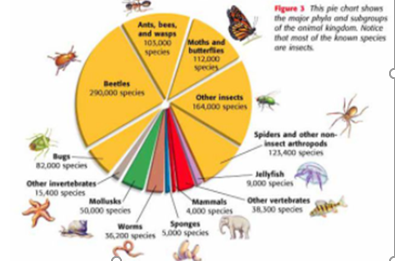
The Diversity of Animals
- There are more than a million different species of animals on earth
- Scientists have organised all these animals according to how they are related
- The animal kingdom is divided into groups called classes
For example: Reptiles, Birds, Mammals
These all have similar features which distinguish them from animals in other classes
Vertebrates
Vertebrates have a back bone
-
Fish

-
Reptiles

-
Birds

Invertebrates
Invertebrates don’t have a back bone
-
Worms

-
Insects

-
Arachnids

The Diversity of Plants
-
Algae

-
Moss

- Flowering Plants

-
Ferns

- Conifers

What is life?
Bio = Living
Biology = Study of living things
There are many different branches of Biology
Zoology = Animals
Botany = Plants
Microbiology = Micro-organisms
Biodiversity = the range of different types of organisms (living things) in an area
Characteristics of Living Things
- Organisation = Organisms are highly organised and are composed of tiny units called cells
- Feed (nutrition)
- Excretion
- Responsiveness (react to their surroundings)
- Reproduce
Not accepted in exam: Growth, respiration, movement
The Definition of Life = The possession of all above characteristics
Metabolism
Metabolism = The chemical reactions that occur in the cells of living organisms
These reactions are responsible for the process of:
- Growth
- Repair
- Responsiveness
- Reproduction
All living things metabolise
There are 2 types of Metabolic Reactions
Anabolic Reactions
These reactions use energy to join small molecules together to form larger molecules
Anabolic: small → big
Example: Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis Formula: Carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light –> C6H12O6 + 6 O2
Catabolic Reactions
These reactions use energy to break down large molecules into smaller ones
Catabolic: small ← big
Example: Respiration
Continuity of Life
Continuity of life is the ability of an organism to exist from generation to the next
You need reproduction and heredity to achieve continuity
Genes are hereditary factors that are passed on from one generation to the next during reproduction
All living things reproduce
Viruses are not living because they don’t have cells (we will come across this again later)
Terminology
| Term | Definition | Examples |
|---|---|---|
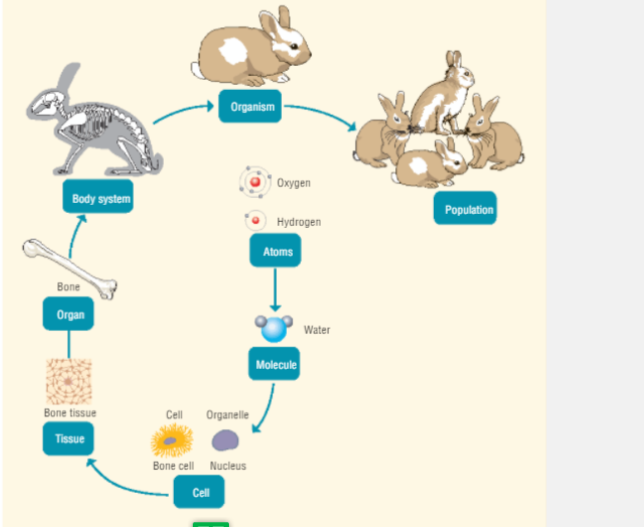
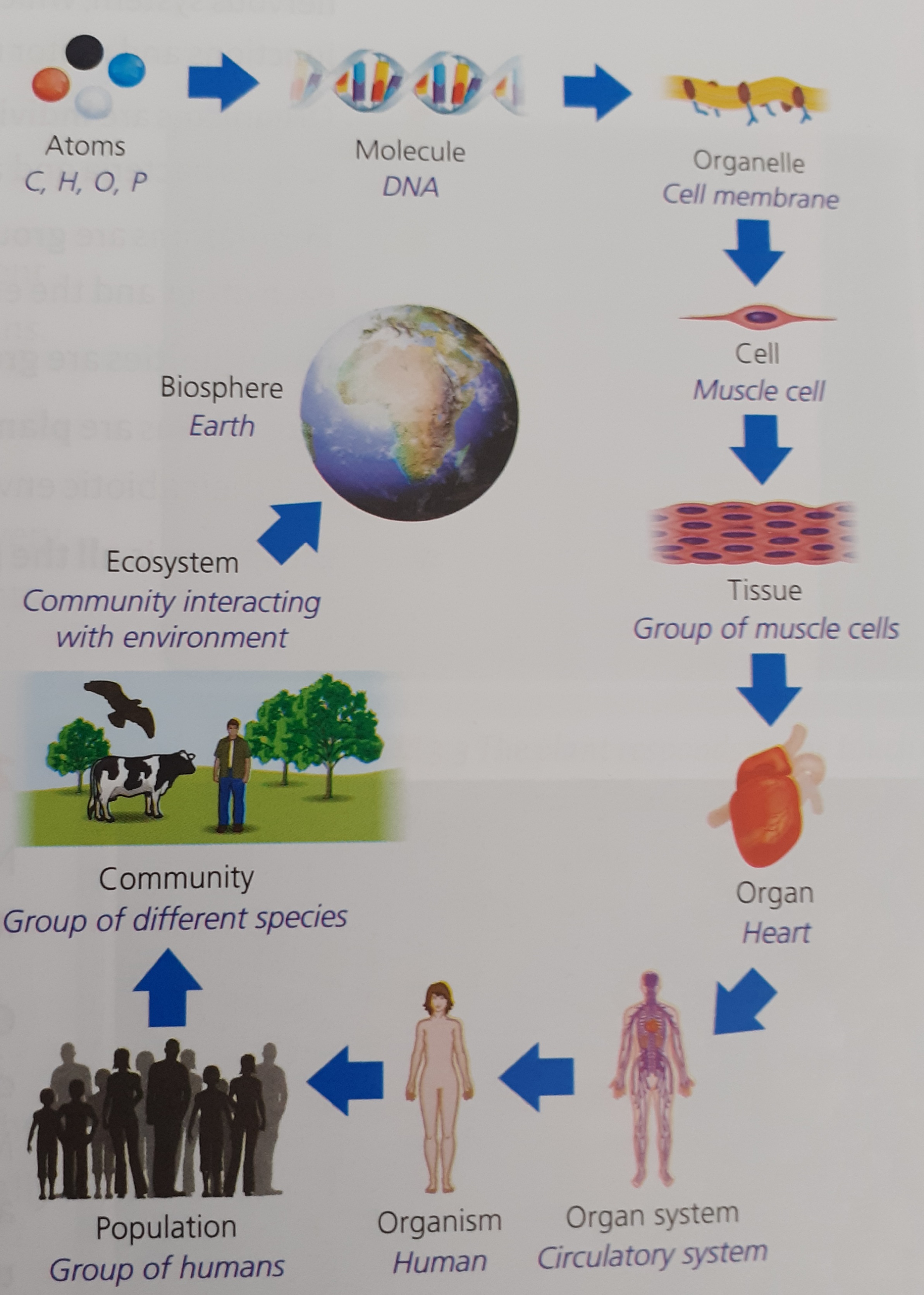
| Organisation | Living things are composed of cells, tissues, organs and organ system | |
| Growth | An increase in the size or number of cells of an organism | |
| Nutrition | The way organism obtain (get) and use food | |
| Excretion | The removal of the waste products of metabolism from the body | |
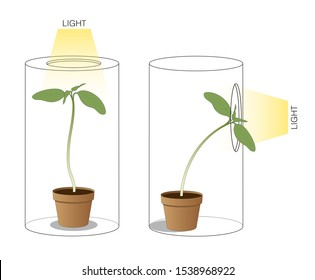
| Response | The activity of a cell or organism as a result of a stimulus | |
| Reproduction | The ability of an organism to make new organisms of the same type | |
| Cells | The basic unit of living things and contain smaller structures called organelles | |
| Tissues | Groups of similar cells working together to carry out a particular function | Muscle tissue and the xylem tissue in plants (the stringy bits in celery) |
| Organs | Groups of different tissues working together to carry out a particular function | Brain and flowers |
| Organ Systems | Groups of organs that work together to carry out a particular function | Circulatory System |
| Organisms | Individual living entities | Unicellular: bacteria, Multicellular: humans |
| Asexual Reproduction | Reproduction that doesn’t require sex cells or fertilisation. Only one parent | |
| Sexual Reproduction | Reproduction that requires sex cells or fertilisation. Two parents | |
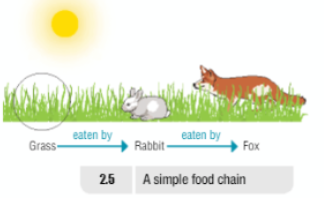
| Herbivore | Animals that only eat plants | Cow |
| Carnivore | Animals that only eat meat | Fox |
| Omnivore | Animals that eat plants and meat | Human |
Organisation Diagrams
Nutrition Diagrams
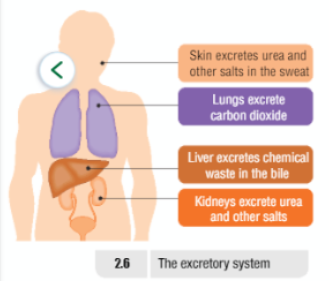
Response Diagram
A mnemonic device to learn all the characteristics of life
| Mnemonic | Word |
|---|---|
| One | Organisation |
| Nutty | Nutrition |
| Elephant | Excretion |
| Ran | Response |
| Riot | Reproduction |
| One nutty elephant ran riot | “Organisation, nutrition, excretion, response, reproduction” |